Microbial Anti-Inflammatory Molecule (MAM) from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Shows a Protective Effect on DNBS and DSS-Induced Colitis Model in Mice through Inhibition of NF-κB Pathway (VSports最新版本)
- PMID: 28203226
- PMCID: PMC5285381 (V体育官网入口)
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00114
Microbial Anti-Inflammatory Molecule (MAM) from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Shows a Protective Effect on DNBS and DSS-Induced Colitis Model in Mice through Inhibition of NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
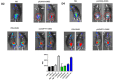
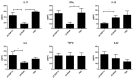
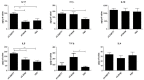
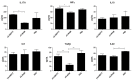
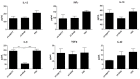
Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and its supernatant showed protective effects in different chemically-induced colitis models in mice. Recently, we described 7 peptides found in the F. prausnitzii supernatant, all belonging to a protein called Microbial Anti-inflammatory Molecule (MAM). These peptides were able to inhibit NF-κB pathway in vitro and showed anti-inflammatory properties in vivo in a DiNitroBenzene Sulfate (DNBS)-induced colitis model. In this current proof we tested MAM effect on NF-κB pathway in vivo, using a transgenic model of mice producing luciferase under the control of NF-κB promoter. Moreover, we tested this protein on Dextran Sodium Sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. To study the effect of MAM we orally administered to the mice a Lactococcus lactis strain carrying a plasmid containing the cDNA of MAM under the control of a eukaryotic promoter VSports手机版. L. lactis delivered plasmids in epithelial cells of the intestinal membrane allowing thus the production of MAM directly by host. We showed that MAM administration inhibits NF-κB pathway in vivo. We confirmed the anti-inflammatory properties of MAM in DNBS-induced colitis but also in DSS model. In DSS model MAM was able to inhibit Th1 and Th17 immune response while in DNBS model MAM reduced Th1, Th2, and Th17 immune response and increased TGFβ production. .
Keywords: Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; Lactococcus lactis; MAM (Microbial Anti-inflammatory Molecule); NF-κB; colitis models; inflammation V体育安卓版. .
Figures
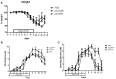
References
-
- Almeida J. F., Mariat D., Azevedo V., Miyoshi A., de Moreno de LeBlanc A., Del Carmen S., et al. . (2014). Correlation between fibronectin binding protein A expression level at the surface of recombinant Lactococcus lactis and plasmid transfer in vitro and in vivo. BMC Microbiol. 14:248. 10.1186/s12866-014-0248-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aubry C., Michon C., Chain F., Chvatchenko Y., Goffin L., Zimmerli S. C., et al. . (2015). Protective effect of TSLP delivered at the gut mucosa level by recombinant lactic acid bacteria in DSS-induced colitis mouse model. Microb. Cell Fact. 14, 176. 10.1186/s12934-015-0367-5 - "V体育安卓版" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chatel J. M., Pothelune L., Ah-Leung S., Corthier G., Wal J. M., Langella P. (2008). In vivo transfer of plasmid from food-grade transiting lactococci to murine epithelial cells. Gene Ther. 15, 1184–1190. 10.1038/gt.2008.59 - "VSports" DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

