Combination therapy with antiangiogenic treatment and photodynamic therapy for the nude mouse bearing U87 glioblastoma
- PMID: 18173712
- PMCID: PMC2766915
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2007.00208.x (VSports)
"VSports在线直播" Combination therapy with antiangiogenic treatment and photodynamic therapy for the nude mouse bearing U87 glioblastoma
Abstract
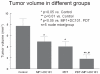
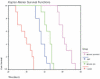
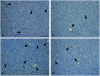
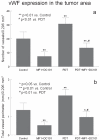
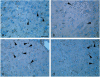
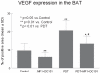
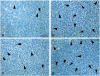
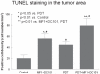
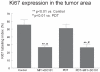
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of combination therapy with photodynamic therapy (PDT) and a novel antiangiogenic regimen using monoclonal antibodies against both vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR)-1 (MF1) and VEGFR-2 (DC101) on intracranial glioblastoma xenografts in nude mice. Nude mice bearing intracerebral U87 glioblastoma were treated with PDT and the antiangiogenic regimen (MF1 and DC101) either alone or in combination, while those left untreated served as tumor controls. Tumor volume and animal survival time were analyzed to evaluate the outcome of different treatment modalities. In addition, the immunohistochemical expression of VEGF in the brain adjacent to the tumor, von Willebrand factor (vWF), apoptotic, and proliferative markers in the tumor area were examined. PDT or MF1 + DC101 alone significantly reduced the tumor volume and prolonged the survival time of glioma-implanted animals VSports手机版. Combined therapy markedly reduced tumor volume and increased survival time with significantly better outcomes than both monotherapies. Both vWF and VEGF levels significantly increased after PDT while they both significantly decreased after antiangiogenic treatment, compared with no treatment. PDT plus antiangiogenic treatment led to significant decreases in both vWF and VEGF expression, compared with PDT alone. Either PDT or antiangiogenic treatment alone significantly increased tumor cell apoptosis compared with no treatment, while combination therapy resulted in further augmentation of apoptosis. Antiangiogenic treatment with or without PDT significantly decreased tumor cell proliferation, compared with either no treatment or PDT alone. In summary, we demonstrate both significant inhibition of tumor growth and extended survival of mice treated by the combination therapy with PDT and antiangiogenic agents, compared with each single treatment, suggesting that the combination therapy may be a promising strategy to improve clinical outcomes in glioblastoma. .
Figures

References
-
- Nicholas MK, Prados MD, Larson DA. Malignant astrocytomas. In: Black PM, Loeffler J, editors. Cancer of the Nervous System. Blackwell Science; Cambridge, MA: 1997. pp. 464–491.
-
- Muller PJ, Wilson BC. Photodynamic therapy of malignant brain tumours. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1990;17:193–198. - PubMed
-
- Pass HI. Photodynamic therapy in oncology: Mechanisms and clinical use. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:443–456. - PubMed
-
- Jiang F, Lilge L, Grenier J, Li Y, Wilson MD, Chopp M. Photodynamic therapy of U87 human glioma in nude rat using liposome-delivered photofrin. Lasers Surg. Med. 1998;22:74–80. - PubMed
-
- Wilson BC. Photodynamic therapy for cancer: Principles. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2002;16:393–396. - PubMed
Publication types (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

