Toxic bile salts induce rodent hepatocyte apoptosis via direct activation of Fas (V体育2025版)
- PMID: 9884343
- PMCID: PMC407865
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI4765
VSports在线直播 - Toxic bile salts induce rodent hepatocyte apoptosis via direct activation of Fas
"VSports app下载" Abstract
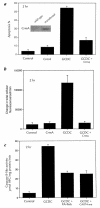
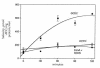
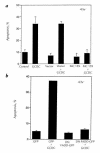
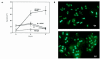
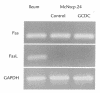
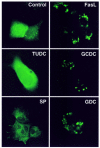
Cholestatic liver injury appears to result from the induction of hepatocyte apoptosis by toxic bile salts such as glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC). Previous studies from this laboratory indicate that cathepsin B is a downstream effector protease during the hepatocyte apoptotic process. Because caspases can initiate apoptosis, the present studies were undertaken to determine the role of caspases in cathepsin B activation. Immunoblotting of GCDC-treated McNtcp. 24 hepatoma cells demonstrated cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and lamin B1 to fragments that indicate activation of effector caspases VSports手机版. Transfection with CrmA, an inhibitor of caspase 8, prevented GCDC-induced cathepsin B activation and apoptosis. Consistent with these results, an increase in caspase 8-like activity was observed in GCDC-treated cells. Examination of the mechanism of GCDC-induced caspase 8 activation revealed that dominant-negative FADD inhibited apoptosis and that hepatocytes isolated from Fas-deficient lymphoproliferative mice were resistant to GCDC-induced apoptosis. After GCDC treatment, immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated Fas oligomerization, and confocal microscopy demonstrated DeltaFADD-GFP (Fas-associated death domain-green fluorescent protein, aggregation in the absence of detectable Fas ligand mRNA. Collectively, these data suggest that GCDC-induced hepatocyte apoptosis involves ligand-independent oligomerization of Fas, recruitment of FADD, activation of caspase 8, and subsequent activation of effector proteases, including downstream caspases and cathepsin B. .
Figures



References
-
- Schmucker DL, Ohta M, Kanai S, Sato Y, Kitani K. Hepatic injury induced by bile salts: correlation between biochemical and morphological events. Hepatology. 1990;12:1216–1221. - PubMed
-
- Greim H, et al. Mechanism of cholestasis. 5. Bile acids in normal rat livers and in those after bile duct ligation. Gastroenterology. 1972;63:837–845. - PubMed
-
- Greim H, et al. Mechanism of cholestasis. 6. Bile acids in human livers with or without biliary obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1972;63:846–850. - PubMed (VSports app下载)
-
- Kwo P, Patel T, Bronk SF, Gores GJ. Nuclear serine protease activity contributes to bile acid-induced apoptosis in hepatocytes. Am J Physiol (Lond) 1995;268:G613–G621. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育官网" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
Substances
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (VSports app下载)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous (V体育平台登录)

