Effects of anserine on oxidative stress and on cell barrier integrity in methylmalonic aciduria
- PMID: 40998969
- PMCID: PMC12464228
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-20600-x
Effects of anserine on oxidative stress and on cell barrier integrity in methylmalonic aciduria
Abstract (VSports手机版)
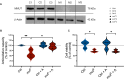
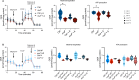
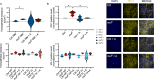
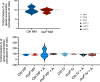
Kidney damage in individuals with methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency (mut0) results from metabolic and oxidative stress, and disrupted mitochondrial homeostasis VSports手机版. Anserine, known for its antioxidant properties and protective effect on cell barrier integrity of endothelial and epithelial kidney and vascular cells, may offer therapeutic potential for chronic disorders. This study explored anserine's effects on immortalized kidney tubular epithelial cells (iKTEC) from mut0 patients. Compared to healthy controls, iKTEC from mut0 patients showed reduced cell viability, antioxidant capacity, oxygen consumption, and ATP production. Expression of the tight junction scaffolding protein zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) was increased in mut0 cells compared to control while transepithelial resistance (TER), and dextran transport (10 kDa) remained unchanged. Anserine treatment restored antioxidant capacity and normalized ZO-1 expression but had no effect on TER or dextran transport. Additionally, cell viability, mitochondrial respiration, and ATP production were unaffected by anserine. Metabolic stress induced by high protein load or disease-associated branched-chain amino acids did not worsen mitochondrial dysfunction or epithelial integrity, and anserine exposure showed no further effects. In conclusion, anserine showed promise in restoring antioxidant capacity in iKTEC from mut0 patients, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent to mitigate ROS, although its effects on mitochondrial function and epithelial integrity warrant further investigation. .
Keywords: Anserine; Human immortalized kidney tubule cell; Metabolic cell stress; Methylmalonic aciduria; Oxidative stress. V体育安卓版.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations V体育ios版. Competing interests: All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Ethical approval: The clinical study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the University of Heidelberg (S-436/2016). Informed consent: All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2013. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
V体育官网 - Figures
References (VSports最新版本)
-
- Matsui, S. M., Mahoney, M. J. & Rosenberg, L. E. The natural history of the inherited methylmalonic acidemias. N. Engl. J. Med.308(15), 857–861. 10.1056/NEJM198304143081501 (1983). - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Hörster, F. et al. Long-term outcome in methylmalonic acidurias is influenced by the underlying defect (mut0, mut-, cblA, cblB). Pediatr. Res.62(2), 225–230. 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3180a0325f (2007). - PubMed
-
- Schumann, A. et al. Mitochondrial damage in renal epithelial cells is potentiated by protein exposure in propionic aciduria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis.44(6), 1330–1342. 10.1002/jimd.12419 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Vardar, A. N. et al. An investigation of different intracellular parameters for inborn errors of metabolism: Cellular stress, antioxidant response and autophagy. Free Radical. Biol. Med.179, 190–199. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.12.312 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources (VSports注册入口)
Full Text Sources
Medical

