"VSports最新版本" Mendelian randomization and transcriptomic data analysis reveals the causal association between gout and breast cancer
- PMID: 40988277
- PMCID: PMC12459518 (VSports在线直播)
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000044305 (V体育平台登录)
Mendelian randomization and transcriptomic data analysis reveals the causal association between gout and breast cancer
Abstract
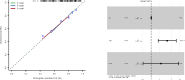
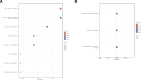
The association between gout and cancer risk has garnered significant interest, particularly in relation to breast cancer, which is the most prevalent cancer among women globally. Nevertheless, the coincidental link between gout and breast cancer, along with its underlying pathogenesis, remains inadequately elucidated. This study utilized publicly available genome-wide association study data from individuals of European ancestry, with sample sizes drawn from multiple genome-wide association study studies, covering genetic variations related to gout and breast cancer. Additionally, transcriptomic data analysis was conducted using datasets from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the Gene Expression Omnibus databases, with the TCGA database comprising 199 adjacent normal tissue samples and 1085 breast cancer tissue samples. Following a rigorous sequence of quality control procedures, we incorporated suitable instrumental variables that exhibited significant associations with the exposure (gout). Five algorithms, namely Mendelian randomization (MR) Egger, weighted median, inverse variance weighting, simple mode, and weighted mode, were employed to deduce the causal link between gout and breast cancer. Moreover, we evaluated the reliability of the MR analysis through heterogeneity and pleiotropy assessments. Subsequently, transcriptomic data analysis was conducted utilizing TCGA and Gene Expression Omnibus databases to explore the possible correlation between gout and breast cancer. MR analysis revealed a stochastic relationship between genetic predisposition to gout and a decreased risk of breast cancer in individuals of European descent (odds ratio: 0. 83, 95% CI: 0. 71-0. 98, P = . 031). Additionally, the sensitivity analysis underscored the strength and reliability of the present MR findings. A key gene (MLX interacting protein-like) was identified using lasso regression methods VSports手机版. The gene showed a strong predictive performance in survival prediction (P < . 05). Our MR study offers evidence indicating that genetic variations linked to gout are causally correlated with a decreased risk of breast cancer in the European population. Furthermore, transcriptomic data analysis indicates that the key gout-associated gene, MLX interacting protein-like, is implicated and holds predictive significance in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. .
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; breast cancer; gout; prognosis; transcriptomic data. V体育安卓版.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc V体育ios版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures (VSports手机版)
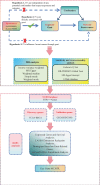

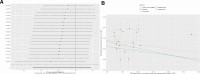
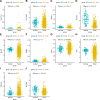
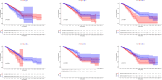

References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–63. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- Loibl S, Poortmans P, Morrow M, Denkert C, Curigliano G. Breast cancer. Lancet. 2021;397:1750–69. - PubMed
-
- Britt KL, Cuzick J, Phillips KA. Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:417–36. - PubMed
-
- de Visser KE, Eichten A, Coussens LM. Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:24–37. - PubMed (V体育官网)
MeSH terms
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育官网" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

