VSports app下载 - Immunomodulation in Pediatric Sepsis: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40364014
- PMCID: PMC12072531
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14092983
Immunomodulation in Pediatric Sepsis: A Narrative Review
V体育官网 - Abstract
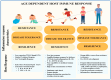
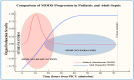
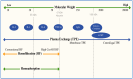
Pediatric sepsis presents a unique clinical challenge due to the distinct characteristics of the developing immune system. The immune response in children differs significantly from that in adults, exhibiting a unique combination of resistance, disease tolerance, and resilience. These factors influence the clinical presentation and prognosis of pediatric patients with sepsis. Over the past few years, various studies have explored the role of immunomodulatory therapies in managing sepsis, including the use of immunoglobulins, corticosteroids, monoclonal antibodies, and immunostimulatory treatments VSports手机版. However, the heterogeneity of the clinical presentations and individual responses makes it difficult to identify universally effective treatments. Recent research has highlighted the importance of a personalized approach based on specific biomarkers and patient phenotyping. Extracorporeal blood purification techniques have emerged as promising strategies for the modulation of hyperinflammation. However, strong evidence supporting their routine use in pediatric sepsis is lacking. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge of the immune response in pediatric sepsis and discusses the main immunomodulatory strategies and future perspectives for personalized therapy. A deeper understanding of the immunological differences between children and adults could improve the prognosis and treatment efficacy, paving the way for new approaches to pediatric sepsis management. .
Keywords: cytokine storm; immune dysfunction; immune modulation; immune paralysis; multiple-organ dysfunction syndrome; pediatric septic shock. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
G. B. has received honoraria for lectures from Jafron® and CytoSorbents®. The other authors have no conflicts to declare V体育ios版.
Figures



VSports - References
-
- Cavaillon J.M., Singer M., Skirecki T. Sepsis therapies: Learning from 30 years of failure of translational research to propose new leads. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020;12:e10128. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201810128. - V体育2025版 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vincent J.L. Improved survival in critically ill patients: Are large RCTs more useful than personalized medicine? No. Intensive Care. Med. 2016;42:1778–1780. doi: 10.1007/s00134-016-4482-5. - "VSports在线直播" DOI - PubMed
-
- Schlapbach L.J., Watson R.S., Sorce L.R., Argent A.C., Menon K., Hall M.W., Akech S., Albers D.J., Alpern E.R., Balamuth F., et al. Society of Critical Care Medicine Pediatric Sepsis Definition Task Force. International Consensus Criteria for Pediatric Sepsis and Septic Shock. JAMA. 2024;331:665–674. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.0179. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sanchez-Pinto L.N., Bennett T.D., DeWitt P.E., Russell S., Rebull M.N., Martin B., Akech S., Albers D.J., Alpern E.R., Balamuth F., et al. Development and Validation of the Phoenix Criteria for Pediatric Sepsis and Septic Shock. JAMA. 2024;331:675–686. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.0196. - DOI (VSports在线直播) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
"VSports注册入口" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

