The activation of the G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor promotes the aggressiveness of MDA-MB231 cells by targeting the IRE1α/TXNIP pathway
- PMID: 39691302
- PMCID: PMC11648343
- DOI: "VSports手机版" 10.4103/RPS.RPS_96_24
The activation of the G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor promotes the aggressiveness of MDA-MB231 cells by targeting the IRE1α/TXNIP pathway
"VSports" Abstract
Background and purpose: This study investigated modulating the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) on the IRElα/TXNIP pathway and its role in drug resistance in MDA-MB231 cells. VSports手机版.
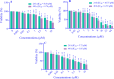
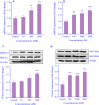
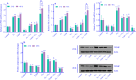
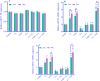
Experimental approach: To determine the optimal concentrations of G1 and 4-hydroxytamoxifen (TAM), GPER expression and ERK1/2 phosphorylation were analyzed using qRT-PCR and western blotting, respectively. Cells were treated with individual concentrations of G1 (1000 nM), G15 (1000 nM), and TAM (2000 nM), as well as combinations of these treatments (G1 + G15, TAM + G15, and G1 + TAM) for 24 and 48 h V体育安卓版. The expression levels of GPER, IRE1α, miR-17-5p, TXNIP, ABCB1, and ABCC1 genes and TXNIP protein expression were evaluated. Finally, apoptosis and cell migration were examined using flow cytometry and the wound-healing assay, respectively. .
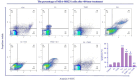
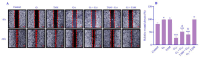
Findings/results: Activating GPER with its specific agonist G1 and TAM significantly increased IRE1α levels in MDA-MB231 cells. IRE1α through splicing XBP1 led to unfolded protein response V体育ios版. In addition, decreased TXNIP gene and protein expression reduced apoptosis, increased migration, and upregulated the genes associated with drug resistance. .
Conclusion and implication: Our investigation revealed that blocking the GPER/IRE1α/TXNIP pathway in MDA-MB231 cells could enhance treatment efficacy and improve chemotherapy responsiveness. The distinct unfolded protein response observed in MDA-MB231 cells may stem from the unique characteristics of these cells, which lack receptors for estrogen, progesterone, and HER2/neu hormones, possessing only the GPER receptor (ER-/PR-/HER2-/GPER+). This study introduced a new pathway in TNBC cells, indicating that targeting GPER could be crucial in comprehensive therapeutic strategies in TNBC cells. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Drug resistance; G protein-coupled estrogen receptor; Thioredoxin interacting protein; Unfolded protein response; miR-17-5P V体育平台登录. .
Copyright: © 2024 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences. VSports注册入口.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest in this study.
V体育官网 - Figures
References
-
- Settacomkul R, Sangpairoj K, Phuagkhaopong S, Meemon K, Niamnont N, Sobhon P, et al. Ethanolic extract of Halymenia durvillei induced G2/M arrest and altered the levels of cell cycle regulatory proteins of MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells. Res Pharm Sci. 2023;18(3):279–291. DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.371584. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kao J, Salari K, Bocanegra M, Choi YL, Girard L, Gandhi J, et al. Molecular profiling of breast cancer cell lines defines relevant tumor models and provides a resource for cancer gene discovery. PLoS One. 2009;4(7):e6146. 1-16. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006146. - VSports最新版本 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育ios版)
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
