"VSports在线直播" Necrostatin-1 Alleviates Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting Necroptosis and Apoptosis of Lung Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 36231101
- PMCID: PMC9563441
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11193139
Necrostatin-1 Alleviates Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting Necroptosis and Apoptosis of Lung Epithelial Cells
"VSports手机版" Abstract
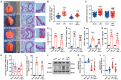
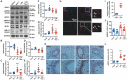
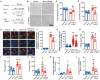
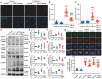
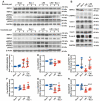
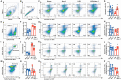
Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury (LIRI) is associated with many diseases, including primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation, and has no specific and effective therapies. Necroptosis contributes to the pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1), the necroptosis inhibitor targeting RIPK1, has been reported to alleviate ischemia-reperfusion injury in various organs VSports手机版. However, the underlying mechanism of Nec-1 in LIRI remains unclear. In this paper, an in vivo LIRI model was built up by left lung hilar clamping in mice, and an in vitro cold ischemia-reperfusion (CI/R) model using BEAS-2B cells was applied to mimic the lung transplantation setting. We found Nec-1 significantly alleviated ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung injury, cytokine releasing, and necroptosis of epithelial cells in mouse lungs. In vitro, Nec-1 also mitigated CI/R-induced cell death and inflammatory responses in BEAS-2B cells, and these protective effects were achieved by simultaneously inhibiting the formation of necrosome and RIPK1-dependent apoptosis. However, Nec-1 decreased the necrosome number but increased the apoptosis level in lung tissues after ischemia reperfusion. We further clarified that Nec-1 could also attenuate lung injury by promoting neutrophil apoptosis from flow cytometry. In conclusion, Nec-1 alleviated lung ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting necroptosis and apoptosis of epithelial cells and promoting the apoptosis of neutrophils. Thus, Nec-1 could be a promising medication against primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. .
Keywords: apoptosis; lung epithelial cells; lung ischemia-reperfusion injury; necroptosis; necrostatin-1. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
"V体育ios版" Figures
References
-
- Diamond J.M., Arcasoy S., Kennedy C.C., Eberlein M., Singer J.P., Patterson G.M., Edelman J.D., Dhillon G., Pena T., Kawut S.M., et al. Report of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Working Group on Primary Lung Graft Dysfunction, part II: Epidemiology, risk factors, and outcomes—A 2016 Consensus Group statement of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017;36:1104–1113. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2017.07.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verleden G.M., Glanville A.R., Lease E.D., Fisher A.J., Calabrese F., Corris P.A., Ensor C.R., Gottlieb J., Hachem R.R., Lama V., et al. Chronic lung allograft dysfunction: Definition, diagnostic criteria, and approaches to treatment-A consensus report from the Pulmonary Council of the ISHLT. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019;38:493–503. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2019.03.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen-Yoshikawa T.F. Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Lung Transplantation. Cells. 2021;10:1333. doi: 10.3390/cells10061333. - DOI (VSports) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Capuzzimati M., Hough O., Liu M. Cell death and ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2022;41:1003–1013. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2022.05.013. - "V体育安卓版" DOI - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports app下载)
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports注册入口" Miscellaneous

