FadA promotes DNA damage and progression of Fusobacterium nucleatum-induced colorectal cancer through up-regulation of chk2
- PMID: 32993749
- PMCID: "V体育官网" PMC7523382
- DOI: "V体育安卓版" 10.1186/s13046-020-01677-w
FadA promotes DNA damage and progression of Fusobacterium nucleatum-induced colorectal cancer through up-regulation of chk2
Abstract
Background: Globally, colorectal cancer (CRC) affects more than 1 million people each year VSports手机版. In addition to non-modifiable and other environmental risk factors, Fusobacterium nucleatum infection has been linked to CRC recently. In this study, we explored mechanisms underlying the role of Fusobacterium nucleatum infection in the progression of CRC in a mouse model. .
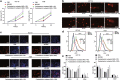
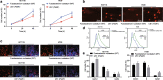
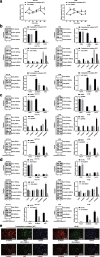
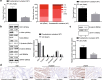
Methods: C57BL/6 J-Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) Min/J mice [APC (Min/+)] were treated with Fusobacterium nucleatum (109 cfu/mL, 0 V体育安卓版. 2 mL/time/day, i. g. , 12 weeks), saline, or FadA knockout (FadA-/-) Fusobacterium nucleatum. The number, size, and weight of CRC tumors were determined in isolated tumor masses. The human CRC cell lines HCT29 and HT116 were treated with lentiviral vectors overexpressing chk2 or silencing β-catenin. DNA damage was determined by Comet assay and γH2AX immunofluorescence assay and flow cytometry. The mRNA expression of chk2 was determined by RT-qPCR. Protein expression of FadA, E-cadherin, β-catenin, and chk2 were determined by Western blot analysis. .
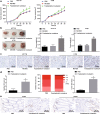
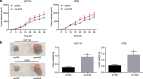
Results: Fusobacterium nucleatum treatment promoted DNA damage in CRC in APC (Min/+) mice. Fusobacterium nucleatum also increased the number of CRC cells that were in the S phase of the cell cycle. FadA-/- reduced tumor number, size, and burden in vivo. FadA-/- also reduced DNA damage, cell proliferation, expression of E-cadherin and chk2, and cells in the S phase V体育ios版. Chk2 overexpression elevated DNA damage and tumor growth in APC (Min/+) mice. .
Conclusions: In conclusion, this study provided evidence that Fusobacterium nucleatum induced DNA damage and cell growth in CRC through FadA-dependent activation of the E-cadherin/β-catenin pathway, leading to up-regulation of chk2 VSports最新版本. .
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; DNA damage; E-cadherin/β-catenin pathway; FadA, chk2; Fusobacterium nucleatum. V体育平台登录.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Newton PT. New insights into niclosamide action: autophagy activation in colorectal cancer. Biochem J. 2019;476:779–781. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190020. - "V体育官网" DOI - PubMed
-
- Antoni S, Soerjomataram I, Moller B, Bray F, Ferlay J. An assessment of GLOBOCAN methods for deriving national estimates of cancer incidence. Bull World Health Organ. 2016;94:174–184. doi: 10.2471/BLT.15.164384. - DOI (VSports最新版本) - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
VSports注册入口 - Substances
Grants and funding (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

