The Vasoactive Mas Receptor in Essential Hypertension
- PMID: 31963731
- PMCID: PMC7019597
- DOI: "V体育官网" 10.3390/jcm9010267
The Vasoactive Mas Receptor in Essential Hypertension
Abstract (VSports手机版)
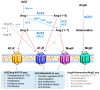
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) has been studied extensively, and with the inclusion of novel components, it has become evident that the system is much more complex than originally anticipated. According to current knowledge, there are two main axes of the RAAS, which counteract each other in terms of vascular control: The classical vasoconstrictive axis, renin/angiotensin-converting enzyme/angiotensin II/angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1R), and the opposing vasorelaxant axis, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor (MasR). An abnormal activity within the system constitutes a hallmark in hypertension, which is a global health problem that predisposes cardiovascular and renal morbidities. In particular, essential hypertension predominates in the hypertensive population of more than 1. 3 billion humans worldwide, and yet, the pathophysiology behind this multifactorial condition needs clarification. While commonly applied pharmacological strategies target the classical axis of the RAAS, discovery of the vasoprotective effects of the opposing, vasorelaxant axis has presented encouraging experimental evidence for a new potential direction in RAAS-targeted therapy based on the G protein-coupled MasR VSports手机版. In addition, the endogenous MasR agonist angiotensin-(1-7), peptide analogues, and related molecules have become the subject of recent studies within this field. Nevertheless, the clinical potential of MasR remains unclear due to indications of physiological-biased activities of the RAAS and interacting signaling pathways. .
Keywords: MasR; angiotensin-(1-7); hypertension; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
"V体育安卓版" References
-
- Bloch M.J. Worldwide prevalence of hypertension exceeds 1.3 billion. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2016;10:753–754. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2016.08.006. - VSports app下载 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mills K.T., Bundy J.D., Kelly T.N., Reed J.E., Kearney P.M., Reynolds K., Chen J., He J. Global disparities of hypertension prevalence and control: A systematic analysis of population-based studies from 90 countries. Circulation. 2016;134:441–450. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018912. - "V体育安卓版" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whelton P.K., Carey R.M., Aronow W.S., Casey D.E., Jr., Collins K.J., Dennison Himmelfarb C., DePalma S.M., Gidding S., Jamerson K.A., Jones D.W., et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2018;138:e426–e483. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000597. - "V体育官网" DOI - PubMed
-
- Rossier B.C., Bochud M., Devuyst O. The hypertension pandemic: An evolutionary perspective. Physiology. 2017;32:112–125. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00026.2016. - "V体育ios版" DOI - PubMed
Publication types (V体育官网入口)
LinkOut - more resources
VSports注册入口 - Full Text Sources

