Dramatic response of BRAF V600E-mutant epithelioid glioblastoma to combination therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitor: establishment and xenograft of a cell line to predict clinical efficacy
- PMID: 31345255
- PMCID: PMC6659204
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-019-0774-7
"VSports手机版" Dramatic response of BRAF V600E-mutant epithelioid glioblastoma to combination therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitor: establishment and xenograft of a cell line to predict clinical efficacy
Abstract
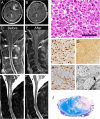
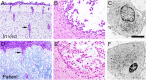
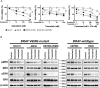
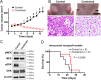
Epithelioid glioblastoma is a rare aggressive variant of glioblastoma (GBM) characterized by a dismal prognosis of about 6 months and frequent leptomeningeal dissemination. A recent study has revealed that 50% of epithelioid GBMs harbor three genetic alterations - BRAF V600E mutation, TERT promoter mutations, and homozygous deletions of CDKN2A/2B. Emerging evidence support the effectiveness of targeted therapies for brain tumors with BRAF V600E mutation. Here we describe a dramatic radiographical response to combined therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors in a patient with epithelioid GBM harboring BRAF V600E mutation, characterized by thick spinal dissemination. From relapsed tumor procured at autopsy, we established a cell line retaining the BRAF V600E mutation, TERT promoter mutation and CDKN2A/2B loss VSports手机版. Intracranial implantation of these cells into mice resulted in tumors closely resembling the original, characterized by epithelioid tumor cells and dissemination, and invasion into the perivascular spaces. We then confirmed the efficacy of treatment with BRAF and MEK inhibitor both in vitro and in vivo. Epithelioid GBM with BRAF V600E mutation can be considered a good treatment indication for precision medicine, and this patient-derived cell line should be useful for prediction of the tumor response and clarification of its biological characteristics. .
Keywords: BRAF V600E; Epithelioid glioblastoma; Precision medicine; Targeted therapy. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References (VSports)
-
- He MX, Wang JJ. Rhabdoid glioblastoma: case report and literature review. Neuropathology. 2011;31:421–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2010.01166.x. - DOI (V体育官网入口) - PubMed
-
- Kleinschmidt-DeMaster BK, Alassiri AH, Birks DK, Newell KL, Moore W, Lillehei KO. Epithelioid versus rhabdoid glioblastomas are distinguished by monosomy 22 and immunohistochemical expression of INI-1 but not claudin 6. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:341–354. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181ce107b. - "V体育平台登录" DOI - PubMed
-
- Momota H, Iwami K, Fujii M, Motomura K, Natsume A, Ogino J, Hasegawa T, Wakabayashi T. Rhabdoid glioblastoma in a child- case report and literature review. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2011;28:65–70. doi: 10.1007/s10014-010-0010-4. - V体育平台登录 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Grants and funding
- 17K16632/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International (VSports app下载)
- 17K17735/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International
- "V体育ios版" 19K18418/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International
- 19K09476/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/International
- R01 NS093079/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
V体育官网入口 - Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

