Catch-up growth, metabolic, and cardiovascular risk in post-institutionalized Romanian adolescents
- PMID: 30323348
- PMCID: PMC6330119
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-018-0196-4
"V体育安卓版" Catch-up growth, metabolic, and cardiovascular risk in post-institutionalized Romanian adolescents
Abstract
Background: Reduced prenatal growth followed by rapid postnatal weight gain are risk factors for developing metabolic and cardiovascular disease. Children reared in institutions experience a similar pattern of growth restriction followed by catch-up growth after removal. We explored whether patterns of catch-up growth affect metabolic and cardiovascular outcomes in previously institutionalized adolescents. VSports手机版.
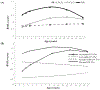
Method: A longitudinal study of institutionalized infants randomized to care as usual (n = 68) or foster care intervention (n = 68), and never institutionalized controls (n = 127) V体育安卓版. Body mass index (BMI) was measured at baseline (20 months), 30, 42 months, and ages 8, 12, 16. At age 16, metabolic and pro-inflammatory markers were derived from blood samples. .
Results: Four BMI trajectories were derived (i. e. , average-stable, low-stable, elevated, and accelerated) V体育ios版. The accelerated trajectory was comprised predominately of children randomized to foster care, who also exhibited higher levels of glycosylated hemoglobin and C-reactive protein than the other three trajectories. Also, children placed in foster care at younger ages were more likely to be on the accelerated rather than the average-stable trajectory. .
Conclusions: Although catch-up growth is viewed as a positive improvement among post-institutionalized children, rapid/continuous increases in body size pose a health concern. Attention should be given to monitoring weight gain, diet, and physical activity. VSports最新版本.
Conflict of interest statement (V体育安卓版)
"VSports最新版本" Figures


V体育2025版 - References
-
- Van IJzendoorn MH, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, Juffer F. Plasticity of growth in height, weight, and head circumference: meta-analytic evidence of massive catch-up after international adoption. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2007;28:334–343. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Sonuga-Barke EJ, Schlotz W, Rutter M. Physical growth and maturation following early severe institutional deprivation: do they mediate specific psychopathological effects?.. Monogr Soc Res Child. 2010; 75:143–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
"V体育ios版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

