VSports手机版 - FXR-Dependent Modulation of the Human Small Intestinal Microbiome by the Bile Acid Derivative Obeticholic Acid
- PMID: 30144429
- PMCID: PMC6279623
- DOI: VSports在线直播 - 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.022
FXR-Dependent Modulation of the Human Small Intestinal Microbiome by the Bile Acid Derivative Obeticholic Acid (V体育安卓版)
Abstract
Background & aims: Intestinal bacteria can modify the composition of bile acids and bile acids, which are regulated by the farnesoid X receptor, affect the survival and growth of gut bacteria. We studied the effects of obeticholic acid (OCA), a bile acid analogue and farnesoid X receptor agonist, on the intestinal microbiomes of humans and mice. VSports手机版.
Methods: We performed a phase I study in 24 healthy volunteers given OCA (5, 10, or 25 mg/d for 17 days). Fecal and plasma specimens were collected at baseline (day 0) and on days 17 (end of dosing) and 37 (end of study). The fecal specimens were analyzed by shotgun meta-genomic sequencing. A Uniref90 high-stringency genomic analysis was used to assign specific genes to the taxonomic signature of bacteria whose abundance was associated with OCA. Male C57BL/6 mice were gavage fed daily with water, vehicle, or OCA (10 mg/kg) for 2 weeks. Small intestine luminal contents were collected by flushing with saline and fecal pellets were collected at baseline and day 14. Mouse samples were analyzed by 16S-tagged sequencing. Culture experiments were performed to determine the taxonomic-specific effects of bile acids and OCA on bacterial growth V体育安卓版. .
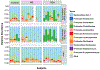
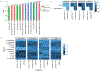
Results: Suppression of endogenous bile acid synthesis by OCA in subjects led to a reversible induction of gram-positive bacteria that are found in the small intestine and are components of the diet and oral microbiota V体育ios版. We found that bile acids decreased proliferation of these bacteria in minimum inhibitory concentration assays. In these organisms, there was an increase in the representation of microbial genomic pathways involved in DNA synthesis and amino acid metabolism with OCA treatment of subjects. Consistent with these findings, mice fed OCA had lower endogenous bile acid levels and an increased proportion of Firmicutes, specifically in the small intestine, compared with mice fed water or vehicle. .
Conclusions: In studying the effects of OCA in humans and mice, we found evidence for interactions between bile acids and features of the small intestinal microbiome. These findings indicate that farnesoid X receptor activation alters the intestinal microbiota and could provide opportunities for microbiome biomarker discovery or new approaches to engineering the human microbiome. ClinicalTrials. gov, NCT01933503. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: Gene Regulation; Genetics; Metabolism; Nuclear Hormone Receptor V体育平台登录. .
Copyright © 2018 AGA Institute VSports注册入口. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. .
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: LA is a consultant for and has stock options in Intercept Pharmaceuticals. FB and JE are employees and shareholders of Intercept Pharmaceuticals. GDW and RMC receive research funding from Intercept Pharmaceuticals V体育官网入口. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
VSports在线直播 - Figures

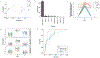


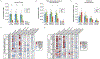
References
-
- Derrien M, van Hylckama Vlieg JE. Fate, activity, and impact of ingested bacteria within the human gut microbiota. Trends Microbiol 2015;23:354–66. - PubMed
-
- van den Bogert B, Erkus O, Boekhorst J, et al. Diversity of human small intestinal Streptococcus and Veillonella populations. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2013;85:376–88. - PubMed (VSports手机版)
-
- Schneider KM, Albers S, Trautwein C. Role of bile acids in the gut-liver axis. Journal of Hepatology 2018;68:1083–1085. - PubMed
-
- Carr RM, Reid AE. FXR agonists as therapeutic agents for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2015;17:500. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育官网)
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (VSports注册入口)
"V体育ios版" Other Literature Sources
Medical

