Tangshen formula improves inflammation in renal tissue of diabetic nephropathy through SIRT1/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 29434819
- PMCID: PMC5776509
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5621
Tangshen formula improves inflammation in renal tissue of diabetic nephropathy through SIRT1/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
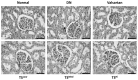
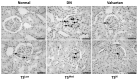
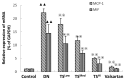
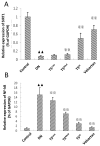
The present study investigated the mechanism underlying the anti-inflammatory effects of Tangshen formula (TS) in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats with diabetic nephropathy (DN). A rat model of DN was established by intraperitoneal injection of 1% (40 mg/kg) streptozotocin and administration of a high fat and glucose diet. Subsequently, SD rats were randomly divided into six groups (n=8): A DN group, a valsartan group, a high-dose TS group, a middle-dose TS group, a low-dose TS group and a control group with normal SD rats. Once rats received their allocated treatment for 12 weeks, body weight and kidney weight were recorded, and fasting blood glucose, ratio of urinary protein, β2-MG and creatinine clearance rate were determined. Furthermore, hemodynamic indices, including plasma viscosity and whole blood reduction viscosity were detected. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the infiltration of macrophages in the kidneys of rats. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting were performed to investigate the activation; mRNA and protein expression levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) in each group. In comparison with the DN group, each biochemical indicator of rats in the high-dose TS group was significantly decreased (P<0. 05). Blood viscosity in each treatment group was significantly decreased when compared with the DN group (P<0. 01). Hematoxylin and eosin staining indicated that the infiltration of macrophages was significantly decreased in the high-dose TS group when compared with the DN group (P<0. 01). mRNA and protein expression levels of MCP-1 and MIF in the high-dose TS group were significantly decreased when compared with the DN group (P<0 VSports手机版. 05). In the treatment groups, SITR1 mRNA expression levels were significantly increased, whereas the mRNA expression levels of NF-κB were significantly decreased (P<0. 01). Western blotting results indicated a significant decrease in the protein expression levels of acetylated NF-κB in the treatment groups when compared with the DN group (P<0. 01) and the propensity of protein expression of the other inflammatory factors were consistent with the mRNA findings. The results of the high-dose TS group were similar to those of the valsartan group. The present study indicates that TS was able to activate SITR1, which lead to NF-κB deacetylation, thus reducing the release of inflammatory factors and decreasing the severity of diabetic nephropathy. .
Keywords: Tangshen formula; diabetic nephropathy; macrophages; nuclear factor-κB; sirtuin V体育安卓版. .
Figures
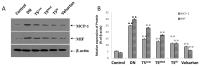
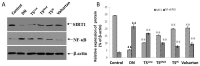
"VSports在线直播" References
-
- Martynyuk L, Martynyuk L, Ruzhitska O, Martynyuk O. Effect of the herbal combination Canephron N on diabetic nephropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: Results of a comparative cohort study. J Altern Complement Med. 2014;20:472–478. doi: 10.1089/acm.2013.0400. - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PubMed
-
- Pan XR, Yang WY, Li GW, Liu J. Prevalence of diabetes and its risk factors in China, 1994. National Diabetes Prevention and Control Cooperative Group. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:1664–1669. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.11.1664. - "VSports手机版" DOI - PubMed
VSports手机版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports最新版本 - Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
