Endothelial Glycocalyx Layer: A Possible Therapeutic Target for Acute Lung Injury during Lung Resection
- PMID: 29423410
- PMCID: PMC5750512
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/5969657
V体育官网 - Endothelial Glycocalyx Layer: A Possible Therapeutic Target for Acute Lung Injury during Lung Resection
Abstract
Background: Shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx layer (EGL) is known to occur during major surgery, but its degradation associated with minimally invasive video-assisted thoracoscopy (VATS) remains unclear VSports手机版. We investigated if serum biomarkers of EGL disruption were elevated during VATS lobectomy, and whether the urinary trypsin inhibitor (UTI) ulinastatin exerted a protective effect during this procedure. .
Materials and methods: Sixty ASA II-III lung cancer patients undergoing elective VATS lobectomy were divided equally into UTI and control groups. UTI group patients received intravenous UTI during surgery. Serum levels of syndecan-1 and heparan sulfate were examined before (T0) and at the end of surgery (T1) V体育安卓版. Serum albumin and hemoglobin were measured before surgery (BOD) and on the first postoperative day (POD1). .
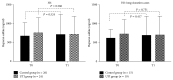
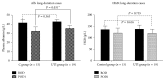
Results: In control group, syndecan-1 levels were significantly elevated at T1 compared with T0 (3 V体育ios版. 77 ± 3. 15 versus 4. 28 ± 3. 30, P = 0. 022⁎) and increased even more significantly in patients whose surgery lasted >3 h (3. 28 ± 2. 84 versus 4. 31 ± 3. 39, P = 0. 003⁎⁎). Serum albumin levels on POD1 were significantly lower in control group compared with UTI group (32. 63 ± 4. 57 versus 35. 76 ± 2. 99, P = 0. 031⁎). .
Conclusion: EGL degradation occurs following VATS lobectomy. UTI can alleviate this shedding, thus helping preserve normal vascular permeability VSports最新版本. .
Trail registration: This trial is registered with ChiCTR-IOC-17010416 (January 13, 2017). V体育平台登录.
Figures

References
-
- Fernández-Pérez E. R., Sprung J., Afessa B., et al. Intra-operative ventilator settings and acute lung injury after elective surgery: a nested case control study. Thorax. 2009;64(2):121–127. doi: 10.1136/thx.2008.102228. - VSports最新版本 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ruffini E., Parola A., Papalia E., et al. Frequency and mortality of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome after pulmonary resection for bronchogenic carcinoma. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 2001;20(1):30–37. doi: 10.1016/S1010-7940(01)00760-6. - DOI (VSports app下载) - PubMed
-
- Licker M. J., Widikker I., Robert J., et al. Operative mortality and respiratory complications after lung resection for cancer: impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and time trends. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 2006;81(5):1830–1837. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.11.048. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Luis Cabezón N., Sánchez Castro I., Bengoetxea Uriarte U. X., Rodrigo Casanova M. P., García Peña J. M., Aguilera Celorrio L. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: A review of the Berlin definition. Revista Española de Anestesiología y Reanimación. 2014;61(6):319–327. doi: 10.1016/j.redar.2014.02.007. - DOI (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
V体育ios版 - Publication types
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
MeSH terms
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports在线直播" Other Literature Sources

