Post-transcriptional Regulation of De Novo Lipogenesis by mTORC1-S6K1-SRPK2 Signaling
- PMID: 29153836
- PMCID: PMC5920692
- DOI: "VSports" 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.037
Post-transcriptional Regulation of De Novo Lipogenesis by mTORC1-S6K1-SRPK2 Signaling
V体育ios版 - Abstract
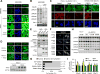
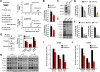
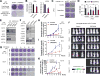
mTORC1 is a signal integrator and master regulator of cellular anabolic processes linked to cell growth and survival. Here, we demonstrate that mTORC1 promotes lipid biogenesis via SRPK2, a key regulator of RNA-binding SR proteins. mTORC1-activated S6K1 phosphorylates SRPK2 at Ser494, which primes Ser497 phosphorylation by CK1. These phosphorylation events promote SRPK2 nuclear translocation and phosphorylation of SR proteins. Genome-wide transcriptome analysis reveals that lipid biosynthetic enzymes are among the downstream targets of mTORC1-SRPK2 signaling. Mechanistically, SRPK2 promotes SR protein binding to U1-70K to induce splicing of lipogenic pre-mRNAs. Inhibition of this signaling pathway leads to intron retention of lipogenic genes, which triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of SRPK2 blunts de novo lipid synthesis, thereby suppressing cell growth. These results thus reveal a novel role of mTORC1-SRPK2 signaling in post-transcriptional regulation of lipid metabolism and demonstrate that SRPK2 is a potential therapeutic target for mTORC1-driven metabolic disorders. VSports手机版.
Keywords: CK1; RNA splicing; RNA stability; S6K1; SR proteins; SRPK2; cancer metabolism; de novo lipid synthesis; mTOR; nonsense-mediated decay V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc V体育ios版. All rights reserved. .
Figures




References
-
- Boersema PJ, Aye TT, van Veen TAB, Heck AJR, Mohammed S. Triplex protein quantification based on stable isotope labeling by peptide dimethylation applied to cell and tissue lysates. Proteomics. 2008;8:4624–4632. - PubMed
-
- Caron A, Richard D, Laplante M. The Roles of mTOR Complexes in Lipid Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015;35:321–348. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y-F, Imam JS, Wilkinson MF. The nonsense-mediated decay RNA surveillance pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007;76:51–74. - PubMed (V体育2025版)
-
- Chen M, Manley JL. Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation: insights from molecular and genomics approaches. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:741–754. - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheong JK, Virshup DM. Casein kinase 1: Complexity in the family. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011;43:465–469. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 HL121266/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- V体育平台登录 - R01 CA046595/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054215/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM114160/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports app下载" R01 CA163591/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- V体育平台登录 - R35 CA197588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062891/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports最新版本" R35 GM122610/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098331/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM051405/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports手机版" R01 GM041890/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL098216/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports注册入口" P30 CA016359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

