Necroptosis regulated proteins expression is an early prognostic biomarker in patient with sepsis: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 29137405
- PMCID: PMC5663577 (VSports)
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21099
"VSports在线直播" Necroptosis regulated proteins expression is an early prognostic biomarker in patient with sepsis: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Background and aim: Increasing researchers indicate that necroptosis is playing an important role in the regulation of systemic inflammatory response syndrome VSports手机版. The current study was to investigate the prognostic biomarker of the regulated proteins of necroptosis in sepsis patients. .
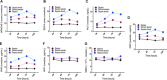
Results: One hundred and twenty-four patients were divided into three groups: 43 patients (34. 68%) with sepsis, 39 patients (31. 45%) with severe sepsis, and 42 patients (33. 87%) with septic shock V体育安卓版. The RIPK3 levels in the severe sepsis and septic shock groups were notably higher than those in sepsis group at various time points (all p < 0. 05), and the RIPK3 levels had positive association with the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score as well as procalcitonin (PCT) level (all p < 0. 05). The RIPK3 level like the SOFA score and PCT level could be a prognostic biomarker of sepsis patients. .
Materials and methods: We prospectively recruited the eligible patients with sepsis, severe sepsis, or septic shock who were treated in our hospital from January 2014 to May 2016. The dynamic changes in infectious variables and blood plasma receptor interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and receptor interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) levels were determined from measurements taken in a double-blinded fashion at 24, 48, 72, and 120 hours later. V体育ios版.
Conclusions: These results suggested that dynamic monitoring of RIPK3 levels can contribute to the prediction of outcome of sepsis and might be of particular value in identifying patients who would benefit from specific treatments. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: biomarker; mortality; receptor interacting protein kinase 1; receptor interacting protein kinase 3; sepsis. V体育平台登录.
V体育平台登录 - Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST We have no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. - "VSports手机版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Seymour CW, Liu VX, Iwashyna TJ, Brunkhorst FM, Rea TD, Scherag A, Rubenfeld G, Kahn JM, Shankar-Hari M, Singer M, Deutschman CS, Escobar GJ, Angus DC. Assessment of Clinical Criteria for Sepsis: For the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:762–774. - VSports app下载 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marshall JC, Vincent JL, Fink MP, Cook DJ, Rubenfeld G, Foster D, Fisher CJ, Jr, Faist E, Reinhart K. Crit Care Med. Vol. 31. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Oct 26, 2000. 2003. Measures, markers, and mediators: toward a staging system for clinical sepsis. A report of the Fifth Toronto Sepsis Roundtable; pp. 1560–1567. - PubMed
-
- Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA. Novel strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nat Med. 2003;9:517–524. - PubMed
-
- Herzum I, Renz H. Inflammatory markers in SIRS, sepsis and septic shock. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15:581–587. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育官网" Medical
Miscellaneous

