Loss of thymic innate lymphoid cells leads to impaired thymopoiesis in experimental graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 28607133
- PMCID: V体育ios版 - PMC5561900
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-01-762658
"VSports app下载" Loss of thymic innate lymphoid cells leads to impaired thymopoiesis in experimental graft-versus-host disease
V体育2025版 - Abstract
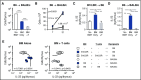
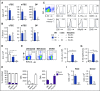
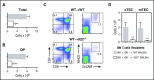
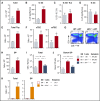
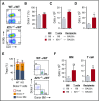
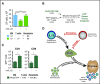
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and posttransplant immunodeficiency are frequently related complications of allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation. Alloreactive donor T cells can damage thymic epithelium, thus limiting new T-cell development. Although the thymus has a remarkable capacity to regenerate after injury, endogenous thymic regeneration is impaired in GVHD. The mechanisms leading to this regenerative failure are largely unknown. Here we demonstrate in experimental mouse models that GVHD results in depletion of intrathymic group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) necessary for thymic regeneration. Loss of thymic ILC3s resulted in deficiency of intrathymic interleukin-22 (IL-22) compared with transplant recipients without GVHD, thereby inhibiting IL-22-mediated protection of thymic epithelial cells (TECs) and impairing recovery of thymopoiesis. Conversely, abrogating IL-21 receptor signaling in donor T cells and inhibiting the elimination of thymic ILCs improved thymopoiesis in an IL-22-dependent fashion. We found that the thymopoietic impairment in GVHD associated with loss of ILCs could be improved by restoration of IL-22 signaling VSports手机版. Despite uninhibited alloreactivity, exogenous IL-22 administration posttransplant resulted in increased recovery of thymopoiesis and development of new thymus-derived peripheral T cells. Our study highlights the role of innate immune function in thymic regeneration and restoration of adaptive immunity posttransplant. Manipulation of the ILC-IL-22-TEC axis may be useful for augmenting immune reconstitution after clinical hematopoietic transplantation and other settings of T-cell deficiency. .
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology. V体育安卓版.
VSports最新版本 - Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests. A patent application has been filed on the use of IL-22 as a thymopoietic growth factor (US 61/487 517) with J. A. D. , A. M. H. , and M. R. M. v. d V体育ios版. B. listed as inventors.
"V体育2025版" Figures
VSports - Comment in
-
Innately interesting interactions.Blood. 2017 Aug 17;130(7):844-845. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-791848. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28818978 No abstract available.
References
-
- van den Brink MR, Alpdogan O, Boyd RL. Strategies to enhance T-cell reconstitution in immunocompromised patients. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4(11):856-867. - PubMed
-
- Na IK, Lu SX, Yim NL, et al. . The cytolytic molecules Fas ligand and TRAIL are required for murine thymic graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(1):343-356. - VSports在线直播 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Krenger W, Holländer GA. The immunopathology of thymic GVHD. Semin Immunopathol. 2008;30(4):439-456. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Krenger W, Rossi S, Holländer GA. Apoptosis of thymocytes during acute graft-versus-host disease is independent of glucocorticoids. Transplantation. 2000;69(10):2190-2193. - PubMed
"VSports在线直播" MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
V体育官网入口 - Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
VSports在线直播 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports在线直播" Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

