The MLL1-H3K4me3 Axis-Mediated PD-L1 Expression and Pancreatic Cancer Immune Evasion
- PMID: 28131992
- PMCID: PMC5291187 (VSports最新版本)
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djw283
"VSports" The MLL1-H3K4me3 Axis-Mediated PD-L1 Expression and Pancreatic Cancer Immune Evasion
V体育官网 - Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is one of the cancers where anti-PD-L1/PD-1 immunotherapy has been unsuccessful. What confers pancreatic cancer resistance to checkpoint immunotherapy is unknown VSports手机版. The aim of this study is to elucidate the underlying mechanism of PD-L1 expression regulation in the context of pancreatic cancer immune evasion. .
Methods: Pancreatic cancer mouse models and human specimens were used to determine PD-L1 and PD-1 expression and cancer immune evasion. Histone methyltransferase inhibitors, RNAi, and overexpression were used to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism of PD-L1 expression regulation. All statistical tests were two-sided. V体育安卓版.
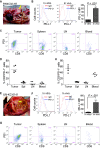
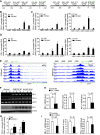
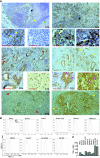
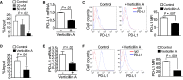
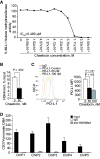
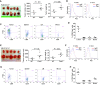
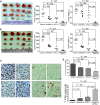
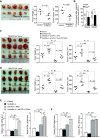
Results: PD-L1 is expressed in 60% to 90% of tumor cells in human pancreatic carcinomas and in nine of 10 human pancreatic cancer cell lines V体育ios版. PD-1 is expressed in 51. 2% to 52. 1% of pancreatic tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Tumors grow statistically significantly faster in FasL-deficient mice than in wild-type mice (P = . 03-. 001) and when CTLs are neutralized (P = . 03-<. 001). H3K4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) is enriched in the cd274 promoter in pancreatic tumor cells. MLL1 directly binds to the cd274 promoter to catalyze H3K4me3 to activate PD-L1 transcription in tumor cells. Inhibition or silencing of MLL1 decreases the H3K4me3 level in the cd274 promoter and PD-L1 expression in tumor cells. Accordingly, inhibition of MLL1 in combination with anti-PD-L1 or anti-PD-1 antibody immunotherapy effectively suppresses pancreatic tumor growth in a FasL- and CTL-dependent manner. .
Conclusions: The Fas-FasL/CTLs and the MLL1-H3K4me3-PD-L1 axis play contrasting roles in pancreatic cancer immune surveillance and evasion. Targeting the MLL1-H3K4me3 axis is an effective approach to enhance the efficacy of checkpoint immunotherapy against pancreatic cancer VSports最新版本. .
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press V体育平台登录. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@qiuluzeuv.cn. .
Figures
V体育官网 - Comment in
-
Epigenetic regulation of PD-L1 expression and pancreatic cancer response to checkpoint immunotherapy. (V体育2025版)Transl Cancer Res. 2017 May;6(Suppl 3):S652-S654. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2017.05.32. Transl Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 30613482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Munir S, Andersen GH, Met O, et al. HLA-restricted CTL that are specific for the immune checkpoint ligand PD-L1 occur with high frequency in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2013;73(6):1764–1776. - PubMed
-
- Hirano F, Kaneko K, Tamura H, et al. Blockade of B7-H1 and PD-1 by monoclonal antibodies potentiates cancer therapeutic immunity. Cancer Res. 2005;65(3):1089–1096. - VSports在线直播 - PubMed
-
- Peng J, Hamanishi J, Matsumura N, et al. Chemotherapy induces programmed cell death-ligand 1 overexpression via the nuclear factor-kappaB to foster an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75(23):5034–5045. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances (VSports手机版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Grants and funding
V体育2025版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
V体育官网入口 - Research Materials
VSports在线直播 - Miscellaneous

