The relevance of using 3D cell cultures, in addition to 2D monolayer cultures, when evaluating breast cancer drug sensitivity and resistance
- PMID: 27304190
- PMCID: PMC5216757 (VSports app下载)
- DOI: VSports手机版 - 10.18632/oncotarget.9935
"VSports" The relevance of using 3D cell cultures, in addition to 2D monolayer cultures, when evaluating breast cancer drug sensitivity and resistance
Abstract
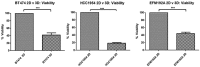
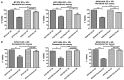
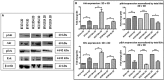
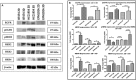
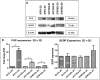
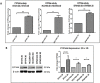
Solid tumours naturally grow in 3D wherein the spatial arrangement of cells affects how they interact with each other. This suggests that 3D cell culture may mimic the natural in vivo setting better than traditional monolayer (2D) cell culture, where cells are grown attached to plastic. Here, using HER2-positive breast cancer cell lines as models (BT474, HCC1954, EFM192A), the effects of culturing cells in 3D using the poly-HEMA method compared to 2D cultures were assessed in terms of cellular viability, response/resistance to anti-cancer drugs, protein expression and enzyme activity. Scanning electron microscopy showed the morphology of cells in 3D to be substantially different to those cultured in 2D. Cell viability in 3D cells was substantially lower than that of cells in 2D cultures, while 3D cultures were more resistant to the effects of HER-targeted (neratinib) and classical chemotherapy (docetaxel) drugs. Expression of proteins involved in cell survival, transporters associated with drug resistance and drug targets were increased in 3D cultures. Finally, activity of drug metabolising enzyme CYP3A4 was substantially increased in 3D compared to 2D cultures. Together this data indicates that the biological information represented by 3D and 2D cell cultures is substantially different i VSports手机版. e. 3D cell cultures demonstrate higher innate resistance to anti-cancer drugs compared to 2D cultures, which may be facilitated by the altered receptor proteins, drug transporters and metabolising enzyme activity. This highlights the importance of considering 3D in addition to 2D culture methods in pre-clinical studies of both newer targeted and more traditional anti-cancer drugs. .
Keywords: 3D cell culture; breast cancer; drug resistance mechanisms; monolayer culture; targeted drugs. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

VSports在线直播 - References
-
- Wilkening S, Stahl F, Bader A. Comparison of primary human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line Hepg2 with regard to their biotransformation properties. Drug metabolism and disposition. 2003;31:1035–1042. - PubMed
-
- Larson B, Cameron G, Hunt S, Long D, Moeller T. The Effect of Cell Culture Method on Long-Term Primary Hepatocyte Cell Health. 2014
-
- Ramaiahgari SC, den Braver MW, Herpers B, Terpstra V, Commandeur JN, van de Water B, Price LS. A 3D in vitro model of differentiated HepG2 cell spheroids with improved liver-like properties for repeated dose high-throughput toxicity studies. Archives of toxicology. 2014;88:1083–1095. - PubMed
-
- Breslin S, O'Driscoll L. Three-dimensional cell culture: the missing link in drug discovery. Drug discovery today. 2013;18:240–249. - V体育官网 - PubMed
-
- Kelm JM, Timmins NE, Brown CJ, Fussenegger M, Nielsen LK. Method for generation of homogeneous multicellular tumor spheroids applicable to a wide variety of cell types. Biotechnology and bioengineering. 2003;83:173–180. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
Substances
"VSports" LinkOut - more resources
V体育官网入口 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
VSports - Miscellaneous

