Andrographolide sulfonate ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by down-regulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways
- PMID: 27175331
- PMCID: PMC4856950
- DOI: "VSports app下载" 10.1016/j.apsb.2016.02.002
Andrographolide sulfonate ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by down-regulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways
Abstract
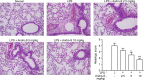
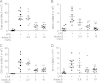
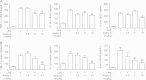
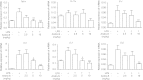
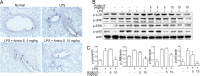
Acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a severe, life-threatening medical condition characterized by widespread inflammation in the lungs, and is a significant source of morbidity and mortality in the patient population. New therapies for the treatment of ALI are desperately needed. In the present study, we examined the effect of andrographolide sulfonate, a water-soluble form of andrographolide (trade name: Xi-Yan-Ping Injection), on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI and inflammation. Andrographolide sulfonate was administered by intraperitoneal injection to mice with LPS-induced ALI. LPS-induced airway inflammatory cell recruitment and lung histological alterations were significantly ameliorated by andrographolide sulfonate. Protein levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and serum were reduced by andrographolide sulfonate administration. mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in lung tissue were also suppressed VSports手机版. Moreover, andrographolide sulfonate markedly suppressed the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) as well as p65 subunit of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). In summary, these results suggest that andrographolide sulfonate ameliorated LPS-induced ALI in mice by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK-mediated inflammatory responses. Our study shows that water-soluble andrographolide sulfonate may represent a new therapeutic approach for treating inflammatory lung disorders. .
Keywords: ALI, acute lung injury; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; Andrographolide sulfonate; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; DSS, dextran sulfate sodium; H&E, hematoxylin & eosin; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; IL-6, interleukin-6; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; Lipopolysaccharide; Lung injury; MAPK; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; Mouse; NF-κB; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; TNBS, trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid; TNF, tumor necrosis factor V体育安卓版. .
VSports最新版本 - Figures
References
-
- Ochiai R. Mechanical ventilation of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Intensive Care. 2015;3:25. - "V体育2025版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Nair G.B., Niederman M.S. Year in review 2013: critical care-respiratory infections. Crit Care. 2014;18:572. - "VSports在线直播" PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen H., Bai C.X., Wang X.D. The value of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory medicine. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010;4:773–783. - "VSports app下载" PubMed
-
- Dreyfuss D., Ricard J.D. Acute lung injury and bacterial infection. Clin Chest Med. 2005;26:105–112. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育平台登录" Full Text Sources
"VSports手机版" Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous (V体育2025版)

