T3D-959: A Multi-Faceted Disease Remedial Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26836193
- PMCID: PMC5577391
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-151013
"VSports手机版" T3D-959: A Multi-Faceted Disease Remedial Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: T3D-959, a dual PPAR-δ/PPAR γ nuclear receptor agonist and former diabetes drug candidate, has been repositioned as an Alzheimer's disease (AD)-modifying therapy VSports手机版. .
Objective: This study examines the effectiveness and mechanisms of T3D-959's therapeutic effects using in vivo and ex vivo rat models of sporadic AD V体育安卓版. .
Methods: A sporadic AD model was generated by intracerebral (i. c. ) administration of streptozotocin (STZ) V体育ios版. Control and i. c. STZ treated rats were gavaged with saline or T3D-959 (0. 3 to 3. 0 mg/kg/day) for 28 days. Spatial learning and memory were evaluated using the Morris water maze test. Frontal lobe slice cultures generated 24 hours after i. c. STZ or vehicle were used to study early effects of T3D-959 (0. 5-1. 0 μM) on viability and molecular markers of AD. .
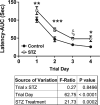
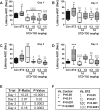
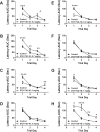
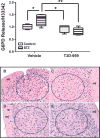
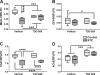
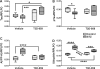
Results: T3D-959 significantly improved spatial learning and memory in i. c STZ-treated rats. Mechanistically, T3D-959 significantly improved culture viability and brain morphology, reduced levels of oxidative stress and Aβ, and normalized expression of phospho-tau, choline acetyltransferase, and myelin-associated glycoprotein VSports最新版本. Protective effects occurred even at the lowest tested dose of T3D-959. .
Conclusions: Pre-clinical proof of concept has been demonstrated that T3D-959 can improve multiple pathologies of AD resulting in significant improvements in cognitive function and molecular and biochemical indices of neurodegeneration. These results support the theses that (1) effective disease modification in AD can be achieved by targeting relevant nuclear receptors, and (2) treating AD as a metabolic disease has the potential to be disease remedial V体育平台登录. A Phase 2a trial of T3D-959 in mild-to-moderate AD patients has been initiated (ClinicalTrials. gov identifier NCT02560753). .
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; PPAR agonist; Streptozotocin; T3D-959; Type 3 diabetes; amyloid; slice culture; spatial learning and memory VSports注册入口. .
"V体育ios版" Figures
References
-
- Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL, Neely TR, Tavares R, Xu XJ, Wands JR, de la Monte SM. Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease–is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimers Dis. 2005;7:63–80. - PubMed
-
- Hoyer S. Is sporadic Alzheimer disease the brain type of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus? A challenging hypothesis. J Neural Transm. 1998;105:415–422. - PubMed
-
- Iwangoff P, Armbruster R, Enz A, Meier-Ruge W. Glycolytic enzymes from human autoptic brain cortex: Normal aged and demented cases. Mech Ageing Dev. 1980;14:203–209. - PubMed
-
- Sims NR, Bowen DM, Smith CC, Flack RH, Davison AN, Snowden JS, Neary D. Glucose metabolism and acetylcholine synthesis in relation to neuronal activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 1980;1:333–336. - VSports - PubMed
V体育平台登录 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports)
Associated data
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
V体育ios版 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

