Successful expansion of functional and stable regulatory T cells for immunotherapy in liver transplantation
- PMID: 26788992
- PMCID: V体育ios版 - PMC4884938
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6927
V体育2025版 - Successful expansion of functional and stable regulatory T cells for immunotherapy in liver transplantation
Abstract
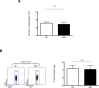
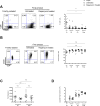
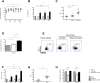
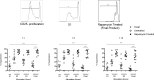
Strategies to prevent organ transplant rejection whilst minimizing long-term immunosuppression are currently under intense investigation with regulatory T cells (Tregs) nearing clinical application. The clinical trial, ThRIL, recently commenced at King's College London, proposes to use Treg cell therapy to induce tolerance in liver transplant recipients, the success of which has the potential to revolutionize the management of these patients and enable a future of drug-free transplants. This is the first report of the manufacture of clinical grade Tregs from prospective liver transplant recipients via a CliniMACS-based GMP isolation technique and expanded using anti-CD3/CD28 beads, IL-2 and rapamycin. We report the enrichment of a pure, stable population of Tregs (>95% CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+)), reaching adequate numbers for their clinical application VSports手机版. Our protocol proved successful in, influencing the expansion of superior functional Tregs, as compared to freshly isolated cells, whilst also preventing their conversion to Th17 cells under pro-inflammatory conditions. We conclude with the manufacture of the final Treg product in the clinical research facility (CRF), a prerequisite for the clinical application of these cells. The data presented in this manuscript together with the much-anticipated clinical results from ThRIL, will undoubtedly inform the improved management of the liver transplant recipient. .
Keywords: Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; immunosuppression; immunotherapy; liver transplantation; regulatory T cells; tolerance. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lerut J, Sanchez-Fueyo A. An appraisal of tolerance in liver transplantation. American journal of transplantation. 2006;6:1774–1780. - PubMed
-
- Benitez C, Londono MC, Miquel R, Manzia TM, Abraldes JG, Lozano JJ, Martinez-Llordella M, Lopez M, Angelico R, Bohne F, Sese P, Daoud F, Larcier P, Roelen DL, Claas F, Whitehouse G, et al. Prospective multicenter clinical trial of immunosuppressive drug withdrawal in stable adult liver transplant recipients. Hepatology. 2013;58:1824–1835. - "VSports" PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. Journal of immunology. 1995;155:1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Khattri R, Cox T, Yasayko SA, Ramsdell F. An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nature immunology. 2003;4:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Sakihama T, Itoh M, Kuniyasu Y, Nomura T, Toda M, Takahashi T. Immunologic tolerance maintained by CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells: their common role in controlling autoimmunity, tumor immunity, and transplantation tolerance. Immunological reviews. 2001;182:18–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms (V体育官网)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/L022699/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K025538/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom (VSports注册入口)
- MR/L008890/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/13/12/30395/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G1002000/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育安卓版" Medical
Research Materials

