"V体育安卓版" Bifidobacterium longum CCM 7952 Promotes Epithelial Barrier Function and Prevents Acute DSS-Induced Colitis in Strictly Strain-Specific Manner
- PMID: 26218526
- PMCID: PMC4517903
- DOI: "V体育官网入口" 10.1371/journal.pone.0134050
Bifidobacterium longum CCM 7952 Promotes Epithelial Barrier Function and Prevents Acute DSS-Induced Colitis in Strictly Strain-Specific Manner (V体育2025版)
Abstract
Background: Reduced microbial diversity has been associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and probiotic bacteria have been proposed for its prevention and/or treatment. Nevertheless, comparative studies of strains of the same subspecies for specific health benefits are scarce. Here we compared two Bifidobacterium longum ssp VSports手机版. longum strains for their capacity to prevent experimental colitis. .
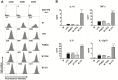
Methods: Immunomodulatory properties of nine probiotic bifidobacteria were assessed by stimulation of murine splenocytes. The immune responses to B. longum ssp. longum CCM 7952 (Bl 7952) and CCDM 372 (Bl 372) were further characterized by stimulation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cell, HEK293/TLR2 or HEK293/NOD2 cells V体育安卓版. A mouse model of dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis was used to compare their beneficial effects in vivo. .
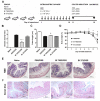
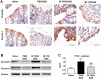
Results: The nine bifidobacteria exhibited strain-specific abilities to induce cytokine production. Bl 372 induced higher levels of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in spleen and dendritic cell cultures compared to Bl 7952. Both strains engaged TLR2 and contain ligands for NOD2 V体育ios版. In a mouse model of DSS-induced colitis, Bl 7952, but not Bl 372, reduced clinical symptoms and preserved expression of tight junction proteins. Importantly, Bl 7952 improved intestinal barrier function as demonstrated by reduced FITC-dextran levels in serum. .
Conclusions: We have shown that Bl 7952, but not Bl 372, protected mice from the development of experimental colitis VSports最新版本. Our data suggest that although some immunomodulatory properties might be widespread among the genus Bifidobacterium, others may be rare and characteristic only for a specific strain. Therefore, careful selection might be crucial in providing beneficial outcome in clinical trials with probiotics in IBD. .
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Here the authors state that Dairy Research Institute Ltd provided support in the form of providing research material, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Furthermore, none of the funding bodies had any role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript V体育平台登录. The fact that the authors' work was funded by several funding bodies and one of the authors is employed by a commercial company does not alter the authors' adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and material.
Figures

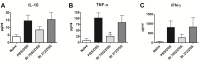
References
-
- Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Crohn's disease. The Lancet. 2012;380(9853):1590–605. 10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60026-9 - "VSports在线直播" DOI - PubMed
-
- Weinstock JV, Elliott DE. Translatability of helminth therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Int J Parasitol. 2013;43(3–4):245–51. Epub 2012/11/28. 10.1016/j.ijpara.2012.10.016 - V体育ios版 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manichanh C, Borruel N, Casellas F, Guarner F. The gut microbiota in IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;9(10):599–608. Epub 2012/08/22. 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.152 . - VSports注册入口 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms (VSports)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports app下载" Other Literature Sources

