Role of non-classical renin-angiotensin system axis in renal fibrosis
- PMID: 25954204
- PMCID: PMC4404823
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00117
Role of non-classical renin-angiotensin system axis in renal fibrosis
Abstract
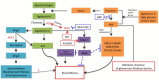
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is a major regulator of renal fibrosis. Besides the classical renin/Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)/angiotensin II (Ang II)/AT1 and AT2 axis, multiple new axes have been recently described. The new members have added new dimensions to RAS, including the ACE2/Ang(1-7)/Mas receptor axis, the prorenin/(pro)renin receptor(PRR)/intracelluar pathway axis, and the Angiotensin A (Ang A), alamandine-Mas-related G protein coupled receptor D(MrgD) axis VSports手机版. This review summarized recent studies regarding role of the non-classical RAS axis in renal fibrosis, and its possible implications to the intervention of progression of chronic kidney disease. .
Keywords: (pro)renin; angiotensin(1–7); angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; renal fibrosis; renin-angiotensin system. V体育安卓版.
Figures
References
-
- Binger K. J., Muller D. N. (2013). Autophagy and the (Pro)renin receptor. Front. Endocrinol. 4:155 10.3389/fendo.2013.00155 - DOI (V体育官网) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brosnihan K. B., Neves L. A., Chappell M. C. (2005). Does the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)/ACE2 balance contribute to the fate of angiotensin peptides in programmed hypertension? Hypertension 46, 1097–1099. 10.1161/01.HYP.0000185149.56516.0a - "V体育ios版" DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
V体育平台登录 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
VSports注册入口 - Research Materials
Miscellaneous