V体育ios版 - Enteric bacteria promote human and mouse norovirus infection of B cells
- PMID: 25378626
- PMCID: PMC4401463
- DOI: V体育ios版 - 10.1126/science.1257147
Enteric bacteria promote human and mouse norovirus infection of B cells
Abstract (VSports注册入口)
The cell tropism of human noroviruses and the development of an in vitro infection model remain elusive. Although susceptibility to individual human norovirus strains correlates with an individual's histo-blood group antigen (HBGA) profile, the biological basis of this restriction is unknown. We demonstrate that human and mouse noroviruses infected B cells in vitro and likely in vivo. Human norovirus infection of B cells required the presence of HBGA-expressing enteric bacteria VSports手机版. Furthermore, mouse norovirus replication was reduced in vivo when the intestinal microbiota was depleted by means of oral antibiotic administration. Thus, we have identified B cells as a cellular target of noroviruses and enteric bacteria as a stimulatory factor for norovirus infection, leading to the development of an in vitro infection model for human noroviruses. .
Copyright © 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science. V体育安卓版.
"VSports手机版" Figures

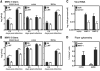

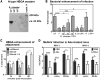
Comment in
-
"V体育平台登录" Virology. Leaping the norovirus hurdle.Science. 2014 Nov 7;346(6210):700-1. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa0607. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Science. 2014. PMID: 25378607 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Koo HL, Ajami N, Atmar RL, DuPont HL. Discov Med. 2010;10:61–70. - "VSports app下载" PMC - PubMed
-
- Glass RI, Parashar UD, Estes MK. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1776–1785. - "V体育2025版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Siebenga JJ, et al. J Infect Dis. 2009;200:802–812. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
V体育官网 - MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

