Modified opsonization, phagocytosis, and killing assays to measure potentially protective antibodies against pneumococcal surface protein A
- PMID: 23925886
- PMCID: PMC3807198
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00371-13 (VSports)
Modified opsonization, phagocytosis, and killing assays to measure potentially protective antibodies against pneumococcal surface protein A (V体育ios版)
V体育2025版 - Abstract
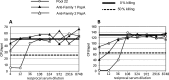
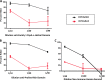
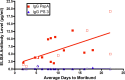
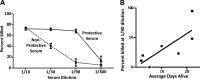
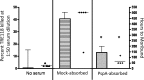
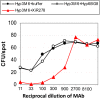
The standard opsonophagocytosis killing assay (OPKA) for antibodies to pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide was modified to permit an evaluation of the protection-mediating antibodies to pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA). We found that by increasing the incubation time with the complement and phagocytes from 45 min to 75 min, the protective activity was readily detected. In another modification, we used a capsule type 2 target strain that expressed PspA but not pneumococcal surface protein C (PspC). With these modifications separately or in combination, rabbit antisera to the recombinant α-helical or proline-rich domains of PspA mediated >50% killing of the target strain. The ability of normal human sera to mediate the killing of pneumococci in this modified OPKA correlated with their levels of antibodies to PspA and their ability to protect mice against fatal infection with a type 3 strain. Passive protection of mice against pneumococci and killing in the modified OPKA were lost when normal human sera were adsorbed with recombinant PspA (rPspA) on Sepharose, thus supporting the potential utility of the modified OPKA to detect protective antibodies to PspA. In the standard OPKA, monoclonal antibodies to PspA were strongly protective in the presence of subprotective amounts of anti-capsule. Thus, the currently established high-throughput OPKA for antibodies to capsule could be modified in one of two ways to permit an evaluation of the opsonic efficacy of antibodies to PspA VSports手机版. .
Figures
References (V体育安卓版)
-
- Wardlaw T, Johannson EW, Hodge M, World Health Organization 2006. Pneumonia: the forgotten killer of children. The United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)/World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva, Switzerland: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9280640489_eng.pdf
-
- Haber M, Barskey A, Baughman W, Barker L, Whitney CG, Shaw KM, Orenstein W, Stephens DS. 2007. Herd immunity and pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a quantitative model. Vaccine 25:5390–5398 - "VSports手机版" PubMed
-
- Hammitt LL, Bruden DL, Butler JC, Baggett HC, Hurlburt DA, Reasonover A, Hennessy TW. 2006. Indirect effect of conjugate vaccine on adult carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae: an explanation of trends in invasive pneumococcal disease. J. Infect. Dis. 193:1487–1494 - PubMed
-
- Scott JR, Millar EV, Lipsitch M, Moulton LH, Weatherholtz R, Perilla MJ, Jackson DM, Beall B, Craig MJ, Reid R, Santosham M, O'Brien KL. 2012. Impact of more than a decade of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine use on carriage and invasive potential in Native American communities. J. Infect. Dis. 205:280–288 - "VSports在线直播" PMC - PubMed
-
- Pilishvili T, Lexau C, Farley MM, Hadler J, Harrison LH, Bennett NM, Reingold A, Thomas A, Schaffner W, Craig AS, Smith PJ, Beall BW, Whitney CG, Moore MR, Active Bacterial Core Surveillance/Emerging Infections Program Network 2010. Sustained reductions in invasive pneumococcal disease in the era of conjugate vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 201:32–41 - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Substances
- "VSports" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

