Bile acid metabolism and signaling
- PMID: 23897684
- PMCID: PMC4422175 (VSports app下载)
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c120023
Bile acid metabolism and signaling
Abstract
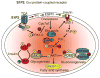
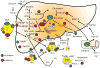
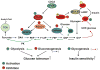
Bile acids are important physiological agents for intestinal nutrient absorption and biliary secretion of lipids, toxic metabolites, and xenobiotics. Bile acids also are signaling molecules and metabolic regulators that activate nuclear receptors and G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling to regulate hepatic lipid, glucose, and energy homeostasis and maintain metabolic homeostasis. Conversion of cholesterol to bile acids is critical for maintaining cholesterol homeostasis and preventing accumulation of cholesterol, triglycerides, and toxic metabolites, and injury in the liver and other organs. Enterohepatic circulation of bile acids from the liver to intestine and back to the liver plays a central role in nutrient absorption and distribution, and metabolic regulation and homeostasis. This physiological process is regulated by a complex membrane transport system in the liver and intestine regulated by nuclear receptors VSports手机版. Toxic bile acids may cause inflammation, apoptosis, and cell death. On the other hand, bile acid-activated nuclear and GPCR signaling protects against inflammation in liver, intestine, and macrophages. Disorders in bile acid metabolism cause cholestatic liver diseases, dyslipidemia, fatty liver diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes. Bile acids, bile acid derivatives, and bile acid sequestrants are therapeutic agents for treating chronic liver diseases, obesity, and diabetes in humans. .
© 2013 American Physiological Society.
Figures





References
-
- Adorini L, Pruzanski M, Shapiro D. Farnesoid X receptor targeting to treat nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Drug Discov Today. 2012;17:988–997. - PubMed
-
- Aldridge MA, Ito MK. Colesevelam hydrochloride: A novel bile acid-binding resin. Ann Pharmacother. 2001;35:898–907. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez L, Jara P, Sanchez-Sabate E, Hierro L, Larrauri J, Diaz MC, Camarena C, De La Vega A, Frauca E, Lopez-Collazo E, Lapunzina P. Reduced hepatic expression of Farnesoid X Receptor in hereditary cholestasis associated to mutation in ATP8B1. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:2451–2460. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports最新版本 - Other Literature Sources
Medical

