Inflammatory monocyte mobilization decreases patient survival in pancreatic cancer: a role for targeting the CCL2/CCR2 axis
- PMID: 23653148
- PMCID: PMC3700620
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0525
"V体育2025版" Inflammatory monocyte mobilization decreases patient survival in pancreatic cancer: a role for targeting the CCL2/CCR2 axis
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the role of the CCL2/CCR2 axis and inflammatory monocytes (CCR2(+)/CD14(+)) as immunotherapeutic targets in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. VSports手机版.
Experimental design: Survival analysis was conducted to determine if the prevalence of preoperative blood monocytes correlates with survival in patients with pancreatic cancer following tumor resection. Inflammatory monocyte prevalence in the blood and bone marrow of patients with pancreatic cancer and controls was compared. The immunosuppressive properties of inflammatory monocytes and macrophages in the blood and tumors, respectively, of patients with pancreatic cancer were assessed. CCL2 expression by human pancreatic cancer tumors was compared with normal pancreas. A novel CCR2 inhibitor (PF-04136309) was tested in an orthotopic model of murine pancreatic cancer. V体育安卓版.
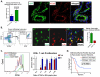
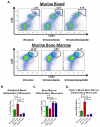
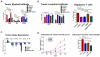
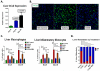
Results: Monocyte prevalence in the peripheral blood correlates inversely with survival, and low monocyte prevalence is an independent predictor of increased survival in patients with pancreatic cancer with resected tumors. Inflammatory monocytes are increased in the blood and decreased in the bone marrow of patients with pancreatic cancer compared with controls. An increased ratio of inflammatory monocytes in the blood versus the bone marrow is a novel predictor of decreased patient survival following tumor resection. Human pancreatic cancer produces CCL2, and immunosuppressive CCR2(+) macrophages infiltrate these tumors V体育ios版. Patients with tumors that exhibit high CCL2 expression/low CD8 T-cell infiltrate have significantly decreased survival. In mice, CCR2 blockade depletes inflammatory monocytes and macrophages from the primary tumor and premetastatic liver resulting in enhanced antitumor immunity, decreased tumor growth, and reduced metastasis. .
Conclusions: Inflammatory monocyte recruitment is critical to pancreatic cancer progression, and targeting CCR2 may be an effective immunotherapeutic strategy in this disease VSports最新版本. .
©2013 AACR.
Figures


"VSports手机版" References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(5):277–300. Epub 2010/07/09. doi: caac.20073 [pii] 10.3322/caac.20073. PubMed PMID: 20610543. - PubMed
-
- Clark CE, Beatty GL, Vonderheide RH. Immunosurveillance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: insights from genetically engineered mouse models of cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009;279(1):1–7. Epub 2008/11/18. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.037. PubMed PMID: 19013709. - PubMed
-
- Clark CE, Hingorani SR, Mick R, Combs C, Tuveson DA, Vonderheide RH. Dynamics of the immune reaction to pancreatic cancer from inception to invasion. Cancer Res. 2007;67(19):9518–27. Epub 2007/10/03. doi: 67/19/9518 [pii] 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0175. PubMed PMID: 17909062. - V体育2025版 - PubMed
-
- Provenzano PP, Cuevas C, Chang AE, Goel VK, Von Hoff DD, Hingorani SR. Enzymatic targeting of the stroma ablates physical barriers to treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(3):418–29. Epub 2012/03/24. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.01.007. PubMed PMID: 22439937; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3371414. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim EJ, Simeone DM. Advances in pancreatic cancer. Current opinion in gastroenterology. 2011;27(5):460–6. Epub 2011/07/23. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e328349e31f. PubMed PMID: 21778878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Grants and funding (V体育2025版)
"VSports最新版本" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
VSports app下载 - Research Materials

