Advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography
- PMID: 23564711
- PMCID: PMC3721049
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.13121193 (V体育ios版)
Advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography (V体育平台登录)
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance (MR) elastography as a method to help diagnose clinically substantial fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and, by using MR elastography as a reference standard, to compare various laboratory marker panels in the identification of patients with NAFLD and advanced fibrosis VSports手机版. .
Materials and methods: This retrospective study was institutional review board approved and HIPAA complaint. Informed consent was waived. This study was conducted in patients with NAFLD, who were identified by imaging characteristics consistent with steatosis in a prospective database that tracks all MR elastographic examinations. Six laboratory-based models of fibrosis were compared with MR elastographic results as well as fibrosis stage from liver biopsy results V体育安卓版. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of each data set were compared. .
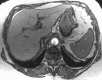
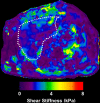
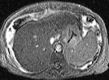
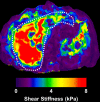
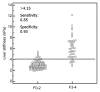
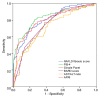
Results: Among 325 patients with NAFLD with MR elastographic data, there were 142 patients who underwent liver biopsy within 1 year of MR elastography. When comparing MR elastography results with liver biopsy results, the best cutoff for advanced fibrosis (stage F3-F4, 46 [32. 4%] of 142) was 4. 15 kPa (AUROC = 0. 954, sensitivity = 0. 85, specificity = 0. 929). This cutoff value identified 104 patients with advanced fibrosis (32. 0% of 325 patients). The FIB-4 score (AUROC = 0. 827) and NAFLD fibrosis score (AUROC = 0. 821) had the best diagnostic accuracy for advanced fibrosis, with high negative predictive values (NAFLD fibrosis score = 0 V体育ios版. 90 and FIB-4 score = 0. 899). .
Conclusion: MR elastography is a useful diagnostic tool for detecting advanced fibrosis in NAFLD. Of the laboratory-based methods, the NAFLD fibrosis and FIB-4 scores can most reliably detect advanced fibrosis VSports最新版本. .
Figures

References
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 2004;40(6):1387–1395 - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
-
- Guha IN, Parkes J, Roderick P, et al. Noninvasive markers of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: validating the European Liver Fibrosis Panel and exploring simple markers. Hepatology 2008;47(2):455–460 - "V体育平台登录" PubMed
-
- Charlton M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of current understanding and future impact. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;2(12):1048–1058 - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 2005;129(1):113–121 - PubMed
-
- Piccinino F, Sagnelli E, Pasquale G, Giusti G. Complications following percutaneous liver biopsy: a multicentre retrospective study on 68,276 biopsies. J Hepatol 1986;2(2):165–173 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Grants and funding
"V体育平台登录" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育安卓版)
Medical
Miscellaneous

