VSports - Endoplasmic reticulum stress modulates liver inflammatory immune response in the pathogenesis of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury
- PMID: 22790388
- PMCID: PMC3414672
- DOI: "VSports" 10.1097/TP.0b013e318259d38e
Endoplasmic reticulum stress modulates liver inflammatory immune response in the pathogenesis of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury
Abstract
Background: Although endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been implicated in the pathophysiology of organ ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), the underlying mechanisms have yet to be fully elucidated. In particular, because tissue proinflammatory immune response is the key mediator of local IRI, how ER stress impacts liver immune cell activation cascade remains to be determined. VSports手机版.
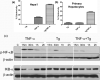
Methods: In vitro, ER stress in macrophages and hepatocytes were induced by pharmacological agents. Macrophage Toll-like receptor 4 and hepatocyte tumor necrosis factor α responses were studied. In vivo, the induction of ER stress by ischemia-reperfusion and the impact of ER stress amelioration by a small molecule chaperon 4-phenylbutyric acid on liver immune response were studied in a murine partial liver warm ischemia model. V体育安卓版.
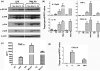
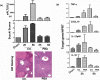
Results: ER-stressed macrophages generated a significantly enhanced proinflammatory immune response against Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation, whereas ER-stressed hepatocytes became more susceptible to tumor necrosis factor α-induced cell death V体育ios版. Ischemia-reperfusion resulted in up-regulations of spliced X-box binding protein 1 and activating transcription factor 6 levels in affected livers. Mice pretreated with 4-phenylbutyric acid were protected from liver IRI, in parallel with diminished local proinflammatory gene induction program. .
Conclusions: Our study documents a potential immune regulatory role of ER stress in the mechanism of liver IRI and provides a rationale for targeting stress response as a new therapeutic means to ameliorate tissue inflammation in organ transplant recipients VSports最新版本. .
Figures

References
-
- Kozutsumi Y, Segal M, Normington K, Gething MJ, Sambrook J. The presence of malfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum signals the induction of glucose-regulated proteins. Nature. 1988;332(6163):462. - PubMed
-
- Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(7):519. - PubMed
-
- Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC. Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(12):1013. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports app下载)
MeSH terms (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

