VSports最新版本 - Resveratrol induces p53-independent, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)-mediated Bax protein oligomerization on mitochondria to initiate cytochrome c release and caspase activation
- PMID: 21712378
- PMCID: PMC3190683
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.202440
Resveratrol induces p53-independent, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)-mediated Bax protein oligomerization on mitochondria to initiate cytochrome c release and caspase activation
Abstract
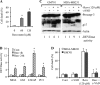
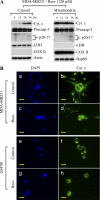
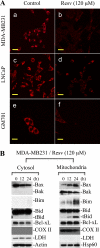
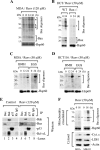
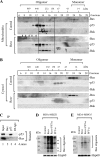
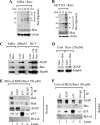
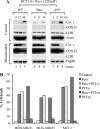
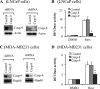
Resveratrol, a naturally occurring phytoalexin, is known to induce apoptosis in multiple cancer cell types, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we show that resveratrol induced p53-independent, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)-mediated translocation of Bax to mitochondria where it underwent oligomerization to initiate apoptosis. Resveratrol treatment promoted interaction between Bax and XIAP in the cytosol and on mitochondria, suggesting that XIAP plays a critical role in the activation and translocation of Bax to mitochondria VSports手机版. This process did not involve p53 but required accumulation of Bim and t-Bid on mitochondria. Bax primarily underwent homo-oligomerization on mitochondria and played a major role in release of cytochrome c to the cytosol. Bak, another key protein that regulates the mitochondrial membrane permeabilization, did not interact with p53 but continued to associate with Bcl-xL. Thus, the proapoptotic function of Bak remained suppressed during resveratrol-induced apoptosis. Caspase-9 silencing inhibited resveratrol-induced caspase activation, whereas caspase-8 knockdown did not affect caspase activity, suggesting that resveratrol induces caspase-9-dependent apoptosis. Together, our findings characterize the molecular mechanisms of resveratrol-induced caspase activation and subsequent apoptosis in cancer cells. .
Figures
References
-
- Mathew R., White E. (2011) Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 21, 113–119 - VSports在线直播 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zois C. E., Koukourakis M. I. (2009) Autophagy 5, 442–450 - PubMed
-
- Blagosklonny M. V. (2002) Int. J. Cancer 98, 161–166 - PubMed
-
- Lowe S. W., Lin A. W. (2000) Carcinogenesis 21, 485–495 - VSports在线直播 - PubMed
-
- Delmas D., Rébé C., Lacour S., Filomenko R., Athias A., Gambert P., Cherkaoui-Malki M., Jannin B., Dubrez-Daloz L., Latruffe N., Solary E. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 41482–41490 - PubMed
"VSports" Publication types
- V体育官网 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
V体育平台登录 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials (V体育安卓版)
Miscellaneous

