V体育安卓版 - Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 p8 protein increases cellular conduits and virus transmission
- PMID: 21076035
- PMCID: PMC2996430
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1009635107
VSports在线直播 - Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 p8 protein increases cellular conduits and virus transmission
Abstract
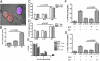
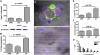
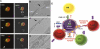
The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is the cause of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma as well as tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-1-associated myelopathy VSports手机版. HTLV-1 is transmitted to T cells through the virological synapse and by extracellular viral assemblies. Here, we uncovered an additional mechanism of virus transmission that is regulated by the HTLV-1-encoded p8 protein. We found that the p8 protein, known to anergize T cells, is also able to increase T-cell contact through lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 clustering. In addition, p8 augments the number and length of cellular conduits among T cells and is transferred to neighboring T cells through these conduits. p8, by establishing a T-cell network, enhances the envelope-dependent transmission of HTLV-1. Thus, the ability of p8 to simultaneously anergize and cluster T cells, together with its induction of cellular conduits, secures virus propagation while avoiding the host's immune surveillance. This work identifies p8 as a viral target for the development of therapeutic strategies that may limit the expansion of infected cells in HTLV-1 carriers and decrease HTLV-1-associated morbidity. .
"V体育官网" Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
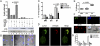
References (V体育ios版)
-
- Poiesz BJ, et al. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1980;77:7415–7419. - PMC (V体育ios版) - PubMed
-
- Gallo RC. The first human retrovirus. Sci Am. 1986;255:88–98. - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
-
- Gessain A, et al. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985;2:407–410. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Ciminale V, et al. Expression and characterization of proteins produced by mRNAs spliced into the X region of the human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type II. Virology. 1995;209:445–456. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
"VSports注册入口" Substances
Grants and funding (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports手机版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

