Curcumin synergizes with resveratrol to inhibit colon cancer
- PMID: 19838927
- PMCID: PMC6370344
- DOI: 10.1080/01635580902752262
Curcumin synergizes with resveratrol to inhibit colon cancer (VSports注册入口)
Abstract (VSports手机版)
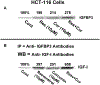
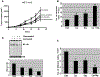
Development and progression of many malignancies, including colorectal cancer, are associated with activation of multiple signaling pathways VSports手机版. Therefore, inhibition of these signaling pathways with noncytotoxic natural products represents a logical preventive and/or therapeutic approach for colon cancer. Curcumin and resveratrol, both of which inhibit the growth of transformed cells and colon carcinogenesis, were selected to examine whether combining them would be an effective preventive and/or therapeutic strategy for colon cancer. Indeed, the combination of curcumin and resveratrol was found to be more effective in inhibiting growth of p53-positive (wt) and p53-negative colon cancer HCT-116 cells in vitro and in vivo in SCID xenografts of colon cancer HCT-116 (wt) cells than either agent alone. Analysis by Calcusyn software showed synergism between curcumin and resveratrol. The inhibition of tumors in response to curcumin and/or resveratrol was associated with the reduction in proliferation and stimulation of apoptosis accompanied by attenuation of NF-kappaB activity. In vitro studies have further demonstrated that the combinatorial treatment caused a greater inhibition of constitutive activation of EGFR and its family members as well as IGF-1R. Our current data suggest that the combination of curcumin and resveratrol could be an effective preventive/therapeutic strategy for colon cancer. .
VSports在线直播 - Figures
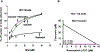
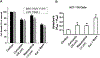

References (V体育平台登录)
-
- Bond JH: Colorectal cancer update: prevention, screening, treatment, and surveillance for high- risk groups. Med Clin North Am 84, 1163–1182, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Salomon OS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, et al.: Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 19, 183–232, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Messa C, Russo F, Caruso MG, et al.: EGF, TGF-a and EGF-R in human colorectal adenocarcinoma. Acta Oncol 37, 285–289, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Harari PM and Huang S-M: Modulation of molecular targets to enhance radiation. Clin Cancer Res 6, 323–325, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Hakam A, Yeatman TJ, Liu L, Mora L, Marcet G, et al.: Expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in human colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol 30, 1128–1133, 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials (V体育平台登录)
Miscellaneous
