Extensions to decision curve analysis, a novel method for evaluating diagnostic tests, prediction models and molecular markers
- PMID: 19036144
- PMCID: PMC2611975 (V体育ios版)
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6947-8-53
V体育官网入口 - Extensions to decision curve analysis, a novel method for evaluating diagnostic tests, prediction models and molecular markers
Abstract
Background: Decision curve analysis is a novel method for evaluating diagnostic tests, prediction models and molecular markers VSports手机版. It combines the mathematical simplicity of accuracy measures, such as sensitivity and specificity, with the clinical applicability of decision analytic approaches. Most critically, decision curve analysis can be applied directly to a data set, and does not require the sort of external data on costs, benefits and preferences typically required by traditional decision analytic techniques. .
Methods: In this paper we present several extensions to decision curve analysis including correction for overfit, confidence intervals, application to censored data (including competing risk) and calculation of decision curves directly from predicted probabilities. All of these extensions are based on straightforward methods that have previously been described in the literature for application to analogous statistical techniques V体育安卓版. .
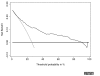
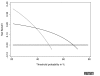
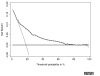
Results: Simulation studies showed that repeated 10-fold crossvalidation provided the best method for correcting a decision curve for overfit. The method for applying decision curves to censored data had little bias and coverage was excellent; for competing risk, decision curves were appropriately affected by the incidence of the competing risk and the association between the competing risk and the predictor of interest. Calculation of decision curves directly from predicted probabilities led to a smoothing of the decision curve. V体育ios版.
Conclusion: Decision curve analysis can be easily extended to many of the applications common to performance measures for prediction models VSports最新版本. Software to implement decision curve analysis is provided. .
Figures (V体育平台登录)





References
-
- Sheridan S, Pignone M, Mulrow C. Framingham-based tools to calculate the global risk of coronary heart disease: a systematic review of tools for clinicians. J Gen Intern Med. 2003;18:1039–1052. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2003.30107.x. - DOI (V体育安卓版) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marchionni L, Wilson RF, Wolff AC, Marinopoulos S, Parmigiani G, Bass EB, Goodman SN. Systematic review: gene expression profiling assays in early-stage breast cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:358–369. - PubMed
-
- Pauker SG, Kassirer JP. The threshold approach to clinical decision making. N Engl J Med. 1980;302:1109–1117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports - Actions
"VSports app下载" Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

