The secretory proprotein convertases furin, PC5, and PC7 activate VEGF-C to induce tumorigenesis
- PMID: 12782675
- PMCID: PMC156106
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI17220
The secretory proprotein convertases furin, PC5, and PC7 activate VEGF-C to induce tumorigenesis
Abstract
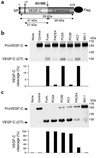
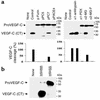
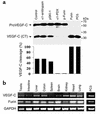
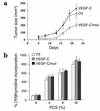
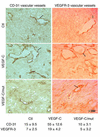
The secretory factor VEGF-C has been directly implicated in various physiological processes during embryogenesis and human cancers. However, the importance of the conversion of its precursor proVEGF-C to mature VEGF-C in tumorigenesis, and vessel formation and the identity of the protease(s) that regulate these processes is/are not known. The intracellular processing of proVEGF-C that occurs within the dibasic motif HSIIRR(227)SL suggests the involvement of the proprotein convertases (PCs) in this process. In addition, furin and VEGF-C were found to be coordinately expressed in adult mouse tissues. Cotransfection of the furin-deficient colon carcinoma cell line LoVo with proVEGF-C and different PC members revealed that furin, PC5, and PC7 are candidate VEGF-C convertases. This finding is consistent with the in vitro digestions of an internally quenched synthetic fluorogenic peptide mimicking the cleavage site of proVEGF-C ((220)Q-VHSIIRR downward arrow SLP(230)). The processing of proVEGF-C is blocked by the inhibitory prosegments of furin, PC5, and PACE4, as well as by furin-motif variants of alpha2-macroglobulin and alpha1-antitrypsin. Subcutaneous injection of CHO cells stably expressing VEGF-C into nude mice enhanced angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, but not tumor growth. In contrast, expression of proVEGF-C obtained following mutation of the cleavage site (HSIIRR(227)SL to HSIISS(227)SL) inhibits angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis as well as tumor growth VSports手机版. Our findings demonstrate the processing of proVEGF-C by PCs and highlight the potential use of PC inhibitors as agents for inhibiting malignancies induced by VEGF-C. .
Figures


References
-
- Huang HY, Ho CC, Huang PH, Hsu SM. Co-expression of VEGF-C and its receptors, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3, in endothelial cells of lymphangioma. Implication in autocrine or paracrine regulation of lymphangioma. Lab. Invest. 2001;81:1729–1734. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- Karkkainen MJ, Makinen T, Alitalo K. Lymphatic endothelium: a new frontier of metastasis research. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:E2–E5. - PubMed
-
- Seidah NG, Chretien M. Proprotein and prohormone convertases: a family of subtilases generating diverse bioactive polypeptides. Brain Res. 1999;848:45–62. - PubMed
V体育ios版 - Publication types
- "V体育2025版" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
V体育官网 - LinkOut - more resources
"VSports app下载" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

