CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production
- PMID: 9670041
- PMCID: PMC2212461
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.2.287
CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production
Abstract (V体育ios版)
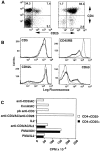
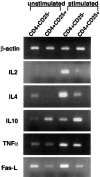
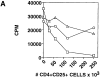
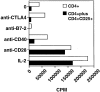
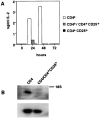
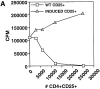
Peripheral tolerance may be maintained by a population of regulatory/suppressor T cells that prevent the activation of autoreactive T cells recognizing tissue-specific antigens. We have previously shown that CD4+CD25+ T cells represent a unique population of suppressor T cells that can prevent both the initiation of organ-specific autoimmune disease after day 3 thymectomy and the effector function of cloned autoantigen-specific CD4+ T cells. To analyze the mechanism of action of these cells, we established an in vitro model system that mimics the function of these cells in vivo. Purified CD4+CD25+ cells failed to proliferate after stimulation with interleukin (IL)-2 alone or stimulation through the T cell receptor (TCR). When cocultured with CD4+CD25- cells, the CD4+CD25+ cells markedly suppressed proliferation by specifically inhibiting the production of IL-2 VSports手机版. The inhibition was not cytokine mediated, was dependent on cell contact between the regulatory cells and the responders, and required activation of the suppressors via the TCR. Inhibition could be overcome by the addition to the cultures of IL-2 or anti-CD28, suggesting that the CD4+CD25+ cells may function by blocking the delivery of a costimulatory signal. Induction of CD25 expression on CD25- T cells in vitro or in vivo did not result in the generation of suppressor activity. Collectively, these data support the concept that the CD4+CD25+ T cells in normal mice may represent a distinct lineage of "professional" suppressor cells. .
V体育官网入口 - Figures



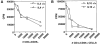

References
-
- Schwartz RH. A cell culture model for T lymphocyte clonal anergy. Science. 1990;248:1349–1356. - PubMed
-
- Miller JFAP, Heath WR. Self-ignorance in the peripheral T-cell pool. Immunol Rev. 1993;133:131–150. - PubMed
-
- Möller, G., editor. 1996. Dominant immunological tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 149:1–243.
-
- Fowell D, Mason D. Evidence that the T cell repertoire of normal rats contains cells with the potential to cause diabetes. Characterization of the CD4+T cell subset that inhibits this autoimmune potential. J Exp Med. 1993;177:627–636. - PMC (V体育官网) - PubMed
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Substances
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
"V体育ios版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育官网" Other Literature Sources
Medical
"V体育2025版" Research Materials

