Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin
- PMID: 9647647
- PMCID: PMC2132999 (VSports app下载)
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.7.1539
Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin
Abstract
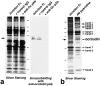
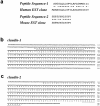
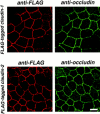
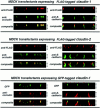
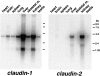
Occludin is the only known integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions (TJ), but recent targeted disruption analysis of the occludin gene indicated the existence of as yet unidentified integral membrane proteins in TJ. We therefore re-examined the isolated junction fraction from chicken liver, from which occludin was first identified. Among numerous components of this fraction, only a broad silver-stained band approximately 22 kD was detected with the occludin band through 4 M guanidine-HCl extraction as well as sonication followed by stepwise sucrose density gradient centrifugation. Two distinct peptide sequences were obtained from the lower and upper halves of the broad band, and similarity searches of databases allowed us to isolate two full-length cDNAs encoding related mouse 22-kD proteins consisting of 211 and 230 amino acids, respectively. Hydrophilicity analysis suggested that both bore four transmembrane domains, although they did not show any sequence similarity to occludin. Immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy revealed that both proteins tagged with FLAG or GFP were targeted to and incorporated into the TJ strand itself. We designated them as "claudin-1" and "claudin-2", respectively. Although the precise structure/function relationship of the claudins to TJ still remains elusive, these findings indicated that multiple integral membrane proteins with four putative transmembrane domains, occludin and claudins, constitute TJ strands VSports手机版. .
Figures






References
-
- Anderson JM, Fanning AS, Lapierre L, Van Itallie CM. Zonula occludens (ZO)-1 and ZO-2: membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologues (MAGuKs) of the tight junction. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995;23:470–475. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:467–475. - PubMed
-
- Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, González S, Cereijido M, Matter K. Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1996;134:1031–1049. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blashcuk OW, Manteuffel RL, Steinberg MS. Purification of desmoglein II: a method for the preparation and fractionation of desmosomal components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;833:426–431. - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Associated data
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育平台登录" Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

