"VSports最新版本" cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors
- PMID: 8962108
- PMCID: PMC26189
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14648 (VSports注册入口)
cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors
"V体育官网入口" Abstract
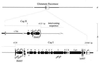
cagA, a gene that codes for an immunodominant antigen, is present only in Helicobacter pylori strains that are associated with severe forms of gastroduodenal disease (type I strains). We found that the genetic locus that contains cagA (cag) is part of a 40-kb DNA insertion that likely was acquired horizontally and integrated into the chromosomal glutamate racemase gene. This pathogenicity island is flanked by direct repeats of 31 bp. In some strains, cag is split into a right segment (cagI) and a left segment (cagII) by a novel insertion sequence (IS605). In a minority of H. pylori strains, cagI and cagII are separated by an intervening chromosomal sequence VSports手机版. Nucleotide sequencing of the 23,508 base pairs that form the cagI region and the extreme 3' end of the cagII region reveals the presence of 19 ORFs that code for proteins predicted to be mostly membrane associated with one gene (cagE), which is similar to the toxin-secretion gene of Bordetella pertussis, ptlC, and the transport systems required for plasmid transfer, including the virB4 gene of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Transposon inactivation of several of the cagI genes abolishes induction of IL-8 expression in gastric epithelial cell lines. Thus, we believe the cag region may encode a novel H. pylori secretion system for the export of virulence determinants. .
VSports - Figures


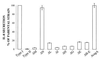
References
-
- Solnick J V, Tompkins L S. Infect Ag Dis. 1993;1:294–309. - PubMed
-
- Parsonnet J, Friedman G D, Vandersteen D P, Chang Y, Vogelman J H, Orentreich N, Sibley R K. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1127–1231. - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
-
- Parsonnet J, Hansen S, Rodriguez L, Gelb A B, Warnke R A, Jellum E, Orentreich N, Vogelman J H, Friedman G D. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1267–1271. - PubMed
-
- Weel J F, van der Hulst R W M, Gerrits Y, Roorda P, Feller M, Dankert J, Tygat N J G, van der Ende A. J Infect Dis. 1996;173:1771–1775. - PubMed
VSports注册入口 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
"VSports手机版" Substances
- VSports - Actions
Associated data
- Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
V体育ios版 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

