BAX-induced cell death may not require interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme-like proteases
- PMID: 8962091
- PMCID: PMC26172
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14559
BAX-induced cell death may not require interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme-like proteases
Abstract
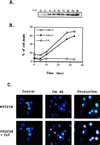
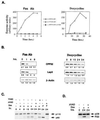
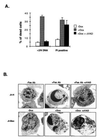
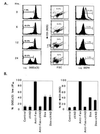
Expression of BAX, without another death stimulus, proved sufficient to induce a common pathway of apoptosis. This included the activation of interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme (ICE)-like proteases with cleavage of the endogenous substrates poly(ADP ribose) polymerase and D4-GDI (GDP dissociation inhibitor for the rho family), as well as the fluorogenic peptide acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-aminotrifluoromethylcoumarin (DEVD-AFC). The inhibitor benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethyl ketone (zVAD-fmk) successfully blocked this protease activity and prevented FAS-induced death but not BAX-induced death. Blocking ICE-like protease activity prevented the cleavage of nuclear and cytosolic substrates and the DNA degradation that followed BAX induction. However, the fall in mitochondrial membrane potential, production of reactive oxygen species, cytoplasmic vacuolation, and plasma membrane permeability that are downstream of BAX still occurred VSports手机版. Thus, BAX-induced alterations in mitochondrial function and subsequent cell death do not apparently require the known ICE-like proteases. .
Figures
References
-
- Oltvai Z N, Milliman C L, Korsmeyer S J. Cell. 1993;74:609–619. - PubMed
-
- Sedlak T W, Oltvai Z N, Yang E, Wang K, Boise L H, Thompson C B, Korsmeyer S J. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:7834–7838. - PMC (VSports app下载) - PubMed
-
- Oltvai Z N, Korsmeyer S J. Cell. 1994;79:189–192. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
-
- Knudson C M, Tung K S, Tourtellotte W G, Brown G A, Korsmeyer S J. Science. 1995;270:96–99. - PubMed
-
- Deckwerth T L, Ellitott J L, Knudson C M, Johnson E M, Snider W D, Korsmeyer S J. Neuron. 1996;17:401–411. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

