V体育安卓版 - Cuproptosis, the novel type of oxidation-induced cell death in thoracic cancers: can it enhance the success of immunotherapy?
- PMID: 39068453
- PMCID: PMC11282696
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01743-2
V体育ios版 - Cuproptosis, the novel type of oxidation-induced cell death in thoracic cancers: can it enhance the success of immunotherapy?
VSports手机版 - Abstract
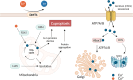
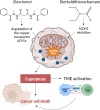
Copper is an important metal micronutrient, required for the balanced growth and normal physiological functions of human organism. Copper-related toxicity and dysbalanced metabolism were associated with the disruption of intracellular respiration and the development of various diseases, including cancer. Notably, copper-induced cell death was defined as cuproptosis which was also observed in malignant cells, representing an attractive anti-cancer instrument. Excess of intracellular copper leads to the aggregation of lipoylation proteins and toxic stress, ultimately resulting in the activation of cell death. Differential expression of cuproptosis-related genes was detected in normal and malignant tissues VSports手机版. Cuproptosis-related genes were also linked to the regulation of oxidative stress, immune cell responses, and composition of tumor microenvironment. Activation of cuproptosis was associated with increased expression of redox-metabolism-regulating genes, such as ferredoxin 1 (FDX1), lipoic acid synthetase (LIAS), lipoyltransferase 1 (LIPT1), dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD), drolipoamide S-acetyltransferase (DLAT), pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 subunit alpha 1 (PDHA1), and pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 subunit beta (PDHB)). Accordingly, copper-activated network was suggested as an attractive target in cancer therapy. Mechanisms of cuproptosis and regulation of cuproptosis-related genes in different cancers and tumor microenvironment are discussed in this study. The analysis of current findings indicates that therapeutic regulation of copper signaling, and activation of cuproptosis-related targets may provide an effective tool for the improvement of immunotherapy regimens. .
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Cuproptosis; Ferredoxin 1 (Fdx1); Immunoediting; Oxidative stress; Tumor microenvironment (TME) V体育安卓版. .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures (V体育2025版)
References
-
- Ruiz LM, Libedinsky A, Elorza AA. Role of copper on mitochondrial function and metabolism. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:711227. 10.3389/fmolb.2021.711227. 10.3389/fmolb.2021.711227 - V体育官网 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
"VSports" Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances (VSports最新版本)
Grants and funding
- 222300420534/Henan Natural Science Foundation of China
- "V体育官网" 222300420534/Henan Natural Science Foundation of China
- 222300420534/Henan Natural Science Foundation of China
- 222300420534/Henan Natural Science Foundation of China
- "VSports注册入口" 222300420534/Henan Natural Science Foundation of China
- 222300420534/Henan Natural Science Foundation of China
- 222300420534/Henan Natural Science Foundation of China (V体育平台登录)
- FFSN-2021-0013/Centre for Collective Use of Institute of Physiologically Active Compounds at Russian Academy of Sciences
- "V体育安卓版" FFSN-2021-0013/Centre for Collective Use of Institute of Physiologically Active Compounds at Russian Academy of Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

