VSports注册入口 - Integrated Omic Analysis Delineates Pathways Modulating Toxic TDP-43 Protein Aggregates in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- PMID: 37174628
- PMCID: PMC10177613
- DOI: "VSports在线直播" 10.3390/cells12091228
Integrated Omic Analysis Delineates Pathways Modulating Toxic TDP-43 Protein Aggregates in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
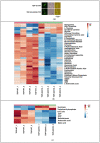
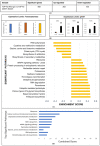
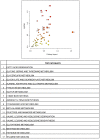
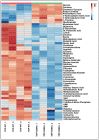
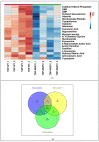
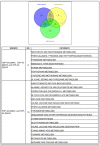
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a multi-systemic, incurable, amyloid disease affecting the motor neurons, resulting in the death of patients. The disease is either sporadic or familial with SOD1, C9orf72, FUS, and TDP-43 constituting the majority of familial ALS. Multi-omics studies on patients and model systems like mice and yeast have helped in understanding the association of various signaling and metabolic pathways with the disease. The yeast model system has played a pivotal role in elucidating the gene amyloid interactions. We carried out an integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of the TDP-43 expressing yeast model to elucidate deregulated pathways associated with the disease. The analysis shows the deregulation of the TCA cycle, single carbon metabolism, glutathione metabolism, and fatty acid metabolism. Transcriptomic analysis of GEO datasets of TDP-43 expressing motor neurons from mice models of ALS and ALS patients shows considerable overlap with experimental results. Furthermore, a yeast model was used to validate the obtained results using metabolite addition and gene knock-out experiments VSports手机版. Taken together, our result shows a potential role for the TCA cycle, cellular redox pathway, NAD metabolism, and fatty acid metabolism in disease. Supplementation of reduced glutathione, nicotinate, and the keto diet might help to manage the disease. .
Keywords: ALS; metabolomics; neurodegenerative disease; protein aggregates; transcriptomics. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


V体育ios版 - References
-
- Blokhuis A.M., Groen E.J.N., Koppers M., Berg L.H.V.D., Pasterkamp R.J. Protein aggregation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;125:777–794. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1125-6. - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McCann E.P., Henden L., Fifita J.A., Zhang K.Y., Grima N., Bauer D.C., Fat S.C.M., Twine N.A., Pamphlett R., Kiernan M.C., et al. Evidence for polygenic and oligogenic basis of Australian sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Med. Genet. 2021;58:87–95. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2020-106866. - DOI - PubMed
"V体育官网" Publication types
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
"VSports手机版" Molecular Biology Databases
"V体育官网入口" Miscellaneous

