Graft-versus-Host Disease Modulation by Innate T Cells
- PMID: 36835495
- PMCID: PMC9962599
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24044084
Graft-versus-Host Disease Modulation by Innate T Cells
Abstract
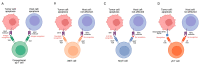
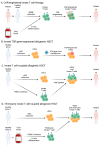
Allogeneic cell therapies, defined by genetically mismatched transplantation, have the potential to become a cost-effective solution for cell-based cancer immunotherapy. However, this type of therapy is often accompanied by the development of graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), induced by the mismatched major histocompatibility complex (MHC) between healthy donors and recipients, leading to severe complications and death VSports手机版. To address this issue and increase the potential for allogeneic cell therapies in clinical practice, minimizing GvHD is a crucial challenge. Innate T cells, encompassing subsets of T lymphocytes including mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells, and gamma delta T (γδ T) cells, offer a promising solution. These cells express MHC-independent T-cell receptors (TCRs), allowing them to avoid MHC recognition and thus GvHD. This review examines the biology of these three innate T-cell populations, evaluates research on their roles in GvHD modulation and allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo HSCT), and explores the potential futures for these therapies. .
Keywords: GvHD modulation; T-cell receptor (TCR); gamma delta T (γδ T) cell; graft-versus-host disease (GvHD); innate T cell; invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell; major histocompatibility complex (MHC); mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cell V体育安卓版. .
VSports注册入口 - Conflict of interest statement
Y. -R. L. and L. Y. are inventors on patents relating to this article filed by UCLA. L. Y. is a scientific advisor to AlzChem and Amberstone Biosciences and a co-founder, stockholder, and advisory board member of Appia Bio V体育ios版. None of the declared companies contributed to or directed any of the research reported in this article. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ruggeri A., Labopin M., Bacigalupo A., Afanasyev B., Cornelissen J.J., Elmaagacli A., Itälä-Remes M., Blaise D., Meijer E., Koc Y., et al. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in HLA matched sibling or matched unrelated donor transplant for patients with acute leukemia, on behalf of ALWP-EBMT. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018;11:40. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0586-4. - "VSports app下载" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blazar B.R., Taylor P.A., Vallera D.A. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells each can utilize a perforin-dependent pathway to mediate lethal graft-versus-host disease in major histocompatibility complex-disparate recipients. Transplantation. 1997;64:571–576. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199708270-00004. - DOI (VSports注册入口) - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
"VSports" MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育2025版" Full Text Sources
Research Materials

