"VSports最新版本" Upregulation of leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein: A key regulator of inflammation and joint fibrosis in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 36569927
- PMCID: PMC9768428
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1028994
Upregulation of leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein: A key regulator of inflammation and joint fibrosis in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative disease of the joints mainly affecting older individuals. Since the etiology behind the progression of OA is not well understood, several associated consequences, such as synovial joint stiffness and its progression due to joint fibrosis, are still poorly understood. Although a lot of developments have been achieved in the diagnosis and management of OA, synovial fibrosis remains one of the major challenging consequences. The present study was therefore focused on understanding the mechanism of synovial fibrosis, which may further contribute to improving symptomatic treatments, leading to overall improvements in the treatment outcomes of patients with OA VSports手机版. .
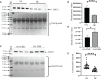
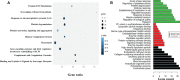
Methods: We used advanced proteomic techniques including isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation and sequential window acquisition of all theoretical mass spectra for the identification of differentially expressed proteins in the plasma samples of patients with OA. An in silico study was carried out to evaluate the association of the identified proteins with their biological processes related to fibrosis and remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The most significantly upregulated protein was then validated by Western blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The target protein was then further investigated for its role in inflammation and joint fibrosis using an in vitro study model V体育安卓版. .
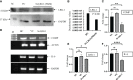
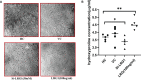
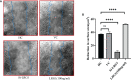
Results: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein (LRG1) was found to be the most highly differentially expressed upregulated (9. 4-fold) protein in the plasma samples of patients with OA compared to healthy controls. The knockdown of LRG1 followed by in vitro studies revealed that this protein promotes the secretion of the ECM in synovial cells and actively plays a role in wound healing and cell migration. The knockdown of LRG1 further confirmed the reduction of the inflammatory- and fibrosis-related markers in primary cells V体育ios版. .
Conclusion: LRG1 was identified as a highly significant upregulated protein in the plasma samples of patients with OA VSports最新版本. It was found to be associated with increased fibrosis and cell migration, leading to enhanced inflammation and joint stiffness in OA pathogenesis. .
Keywords: SWATH; biomarker; fibrosis; iTRAQ; inflammation; leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; osteoarthritis. V体育平台登录.
Copyright © 2022 Sarkar, Chakraborty, Kumar, Malhotra and Biswas. VSports注册入口.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
VSports手机版 - Figures
References
-
- Martel-Pelletier J, Barr AJ, Cicuttini FM, Conaghan PG, Cooper C, Goldring MB, et al. . Osteoarthritis. In: Nature reviews disease primers. United kingdom: Nature Publishing Group; (2016). 2:1–18. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/nrdp201672 (V体育官网入口). - PubMed
-
- Watt FE. Osteoarthritis biomarkers: year in review. Osteoarthr Cartil [Internet] (2018) 26(3):312–8. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2017.10.016 - "VSports" DOI - PubMed
-
- Braun HJ, Gold GE. Diagnosis of osteoarthritis: Imaging. Bone (2012) 51(2):278–88. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.11.019 - DOI (VSports app下载) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
VSports最新版本 - Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

