Inhibitory effect of CUL1 on atherosclerosis through the p53 pathway
- PMID: 36267727
- PMCID: PMC9577759 (V体育2025版)
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-4372
Inhibitory effect of CUL1 on atherosclerosis through the p53 pathway
VSports app下载 - Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis (AS) is a serious chronic condition associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases VSports手机版. Research on AS is currently lacking, and there is a need to increase research to improve the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of AS. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to explore the molecular mechanism and identify potential biomarkers in AS. .
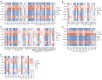
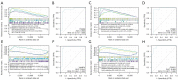
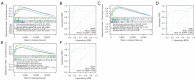
Methods: First, we downloaded the GSE28829 dataset and screened differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Then, DEGs were analyzed by functional enrichment analysis and protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks to determine hub genes. The key gene for AS was identified following the expression analysis of AS, clinical correlation with immune factors, the gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) enrichment pathway, and receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis V体育安卓版. In functional experiments, correlations between cullin 1 (CUL1), cytokines, and downstream targets in AS were investigated. .
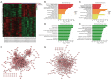
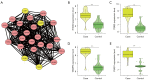
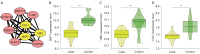
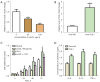
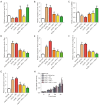
Results: We identified 595 upregulated and 391 downregulated DEGs enriched in neutrophil degranulation, the B-cell receptor signaling pathway, cell-matrix adhesion, and fatty acid degradation V体育ios版. Through PPI, we identified 7 hub genes for the expression analysis, immunoassay, and GSEA. Finally, CUL1 was identified as the inhibitory gene in AS associated with immune factors, and was found to have a strong prognostic prediction ability. The results indicated that CUL1 upregulated interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α concentrations, and weakened the cell proliferation of AS. It was also found that CUL1 exerted its inhibitory function in AS by the p53 pathway. .
Conclusions: The findings of the present study indicate that CUL1 is a suppressing gene in AS, and has the potential to be a therapeutic and prognostic biomarker for AS VSports最新版本. .
Keywords: Atherosclerosis (AS); cullin 1 (CUL1); differentially expressed genes; immunoassay; p53 pathway. V体育平台登录.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine VSports注册入口. All rights reserved. .
VSports最新版本 - Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm V体育官网入口. amegroups. com/article/view/10. 21037/atm-22-4372/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
V体育安卓版 - References
-
- Zheng X. Research progress on the relationship between sphingomyelin signaling pathway and atherosclerosis. Chinese Journal of Arteriosclerosis 2019;27:87-92.
-
- Xie S, Cheng W, Zhu J, et al. Research Progressonon the Mechanism of Atherosclerosis. World Journal of Complex Medicine 2016;2:85-90.
-
- Carmeliet P, Hicklin DJ, Fang L, et al. Method of treating atherosclerosis and other inflammatory diseases: WO, EP1515707 A2[P]. 2005.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials (V体育官网)
Miscellaneous
