Prognostic analysis of cuproptosis-related gene in triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 35979353
- PMCID: "VSports在线直播" PMC9376234
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.922780
Prognostic analysis of cuproptosis-related gene in triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Cuproptosis is a copper-dependent cell death mechanism that is associated with tumor progression, prognosis, and immune response. However, the potential role of cuproptosis-related genes (CRGs) in the tumor microenvironment (TME) of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains unclear VSports手机版. .
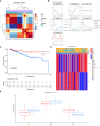
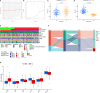
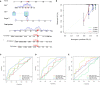
Patients and methods: In total, 346 TNBC samples were collected from The Cancer Genome Atlas database and three Gene Expression Omnibus datasets, and were classified using R software packages. The relationships between the different subgroups and clinical pathological characteristics, immune infiltration characteristics, and mutation status of the TME were examined. Finally, a nomogram and calibration curve were constructed to predict patient survival probability to improve the clinical applicability of the CRG_score. V体育安卓版.
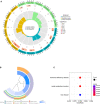
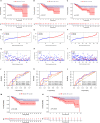
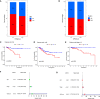
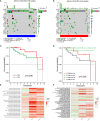
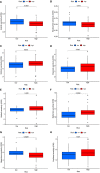
Results: We identified two CRG clusters with immune cell infiltration characteristics highly consistent with those of the immune-inflamed and immune-desert clusters. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the gene signature can be used to evaluate tumor immune cell infiltration, clinical features, and prognostic status. Low CRG_scores were characterized by high tumor mutation burden and immune activation, good survival probability, and more immunoreactivity to CTLA4, while high CRG_scores were characterized by the activation of stromal pathways and immunosuppression V体育ios版. .
Conclusion: This study revealed the potential effects of CRGs on the TME, clinicopathological features, and prognosis of TNBC VSports最新版本. The CRGs were closely associated with the tumor immunity of TNBC and are a potential tool for predicting patient prognosis. Our data provide new directions for the development of novel drugs in the future. .
Keywords: cuproptosis; immunotherapy; triple-negative breast cancer; tumor microenvironment; tumor mutation burden. V体育平台登录.
Copyright © 2022 Sha, Si, Wu, Chen, Xiong, Xu, Liu, Mei, Wang and Li VSports注册入口. .
"V体育ios版" Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kumar P, Aggarwal R. An overview of triple-negative breast cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet (2016) 293(2):247–69. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3859-y - "V体育官网" DOI - PubMed
-
- Gupta GK, Collier AL, Lee D, Hoefer RA, Zheleva V, Siewertsz van Reesema LL, et al. . Perspectives on triple-negative breast cancer: Current treatment strategies, unmet needs, and potential targets for future therapies. Cancers (Basel) (2020) 12(9):2392. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092392 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
VSports app下载 - Substances
LinkOut - more resources (VSports在线直播)
VSports app下载 - Full Text Sources

