The Role of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Autoimmune Disease: A Potential Target
- PMID: 35844539
- PMCID: "VSports app下载" PMC9284064
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.871713
The Role of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Autoimmune Disease: A Potential Target (V体育ios版)
Abstract (V体育平台登录)
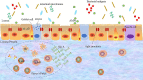
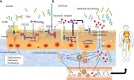
Autoimmune diseases are a series of diseases involving multiple tissues and organs, characterized by the over production of abnormal multiple antibodies. Although most studies support that the impaired immune balance participates in the development of autoimmune diseases, the specific pathogenesis of it is not fully understood. Intestinal immunity, especially the intestinal mucosal barrier has become a research hotspot, which is considered to be an upstream mechanism leading to the impaired immune balance VSports手机版. As an important defense barrier, the intestinal mucosal barrier regulates and maintains the homeostasis of internal environment. Once the intestinal barrier function is impaired under the effect of multiple factors, it will destroy the immune homeostasis, trigger inflammatory response, and participate in the development of autoimmune diseases in the final. However, the mechanism of the intestinal mucosal barrier how to regulate the homeostasis and inflammation is not clear. Some studies suggest that it maintains the balance of immune homeostasis through the zonulin pathway, intestinal microbiome, and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Our review focused on the composition and the function of the intestinal mucosal barrier to describe the research progress of it in regulating the immune homeostasis and inflammation, and also pointed that the intestinal mucosal barrier was the potential targets in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. .
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; intestinal microbiome; intestinal mucosal barrier; toll-like receptors signal pathway; zonulin pathway V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2022 An, Liu, Wang, Fan, Hu, Zhang, Yang and Chen V体育ios版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a the potential conflict of interest.
"V体育2025版" Figures
References
-
- Khan MF, Wang H. Environmental Exposures and Autoimmune Diseases: Contribution of Gut Microbiome. Front Immunol (2019) 10:3094. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03094 - "VSports在线直播" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
"VSports在线直播" MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports在线直播" Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

