V体育ios版 - Amelioration of type 2 diabetes by the novel 6, 8-guanidyl luteolin quinone-chromium coordination via biochemical mechanisms and gut microbiota interaction
- PMID: 35700921
- PMCID: PMC10105086 (VSports在线直播)
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.06.003
Amelioration of type 2 diabetes by the novel 6, 8-guanidyl luteolin quinone-chromium coordination via biochemical mechanisms and gut microbiota interaction
Abstract
Introduction: Luteolin is a plant-derived flavonoid that exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities. Studies on luteolin have mainly focused on its use for hyperlipidaemia prevention, whereas the capacity of the flavonoid to hinder hyperglycaemia development remains underexplored VSports手机版. .
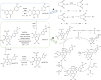
Objectives: To probe the anti-hyperglycemic mechanism of 6,8-guanidyl luteolin quinone-chromium coordination (GLQ. Cr), and to assess its regulatory effect on intestinal microbiota in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) mice V体育安卓版. .
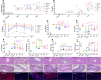
Methods: High-sucrose/high-fat diet-induced and intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin was used to develop a T2DM model. Glycometabolism related indicators, histopathology, and gut microbiota composition in caecum samples were evaluated, and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) of liver samples was conducted V体育ios版. Faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) was further used to verify the anti-hyperglycemic activity of intestinal microbiota. .
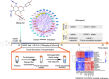
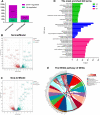
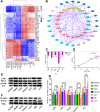
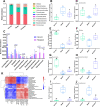
Results: The administration of GLQ. Cr alleviated hyperglycaemia symptoms by improving liver and pancreatic functions and modulating gut microbe communities (Lactobacillus, Alistipes, Parabacteroides, Lachnoclostridium, and Desulfovibrio). RNA-seq analysis showed that GLQ VSports最新版本. Cr mainly affected the peroxisome proliferative activated receptor (PPAR) signalling pathway in order to regulate abnormal glucose metabolism. FMT significantly modulated the abundance of Lactobacillus, Alloprevotella, Alistipes, Bacteroides, Ruminiclostridium, Brevundimonas and Pseudomonas in the caecum to balance blood glucose levels and counteract T2DM mice inflammation. .
Conclusion: GLQ V体育平台登录. Cr improved the abnormal glucose metabolism in T2DM mice by regulating the PPAR signalling pathway and modulating intestinal microbial composition. FMT can improve the intestinal microecology of the recipient and in turn ameliorate the symptoms of T2DM-induced hyperglycaemia. .
Keywords: Anti-hyperglycemic; Faecal microbiota transplantation; Intestinal microbiota; Luteolin; RNA-seq. VSports注册入口.
Copyright © 2023. Production and hosting by Elsevier B. V. V体育官网入口.
"V体育ios版" Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- van der Klaauw A.A., Keogh J.M., Henning E., Stephenson C., Kelway S., Trowse V.M., et al. Divergent effects of central melanocortin signalling on fat and sucrose preference in humans. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1) doi: 10.1038/ncomms13055. - "V体育安卓版" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao C., Yang C., Wai S.T.C., Zhang Y., P. Portillo M., Paoli P., et al. Regulation of glucose metabolism by bioactive phytochemicals for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(6):830–847. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1501658. - VSports注册入口 - DOI - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation . 9th ed. Busan, Korea; International Diabetes Federation: 2019. IDF Diabetes Atlas.
-
- Yan X., Yang C., Lin G., Chen Y., Miao S., Liu B., et al. Antidiabetic potential of green seaweed Enteromorpha prolifera flavonoids regulating insulin signaling pathway and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. J Food Sci. 2019;84(1):165–173. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14415. - "VSports" DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
VSports最新版本 - Full Text Sources
Medical

