"VSports" Celastrol induces ferroptosis in activated HSCs to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis via targeting peroxiredoxins and HO-1
- PMID: 35646542
- PMCID: PMC9136576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.12.007
"VSports app下载" Celastrol induces ferroptosis in activated HSCs to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis via targeting peroxiredoxins and HO-1
Abstract
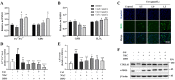
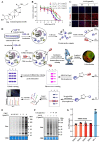
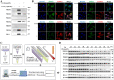
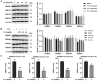
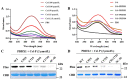
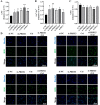
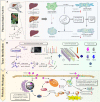
Ferroptosis is a form of regulated cell death, characterized by excessive membrane lipid peroxidation in an iron- and ROS-dependent manner. Celastrol, a natural bioactive triterpenoid extracted from Tripterygium wilfordii, shows effective anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory activities in multiple hepatic diseases VSports手机版. However, the exact molecular mechanisms of action and the direct protein targets of celastrol in the treatment of liver fibrosis remain largely elusive. Here, we discover that celastrol exerts anti-fibrotic effects via promoting the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inducing ferroptosis in activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). By using activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) in combination with bio-orthogonal click chemistry reaction and cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA), we show that celastrol directly binds to peroxiredoxins (PRDXs), including PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX4 and PRDX6, through the active cysteine sites, and inhibits their anti-oxidant activities. Celastrol also targets to heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) and upregulates its expression in activated-HSCs. Knockdown of PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX4, PRDX6 or HO-1 in HSCs, to varying extent, elevated cellular ROS levels and induced ferroptosis. Taken together, our findings reveal the direct protein targets and molecular mechanisms via which celastrol ameliorates hepatic fibrosis, thus supporting the further development of celastrol as a promising therapeutic agent for liver fibrosis. .
Keywords: ABPP; ABPP, activity-based protein profiling; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; Anti-oxidant; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; CETSA, cellular thermal shift assay; COL1A1, collagen type I alpha-1; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; Cel-P, celastrol-probe; Celastrol; ECM, extracellular matrix; Ferroptosis; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HMGB1, high mobility group protein B1; HO-1; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; Hepatic fibrosis; LPO, lipid peroxidation; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor γ; PRDXs, peroxiredoxins; Peroxiredoxin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Reactive oxygen species; VDACs, voltage-dependent anion channels; VIM, vimentin; α-SMA, alpha smooth muscle actin V体育安卓版. .
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences V体育ios版. Production and hosting by Elsevier B. V. .
"V体育官网入口" Figures



References (V体育官网入口)
-
- Lim Y.S., Kim W.R. The global impact of hepatic fibrosis and end-stage liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2008;12:733–746, vii. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Ellis E.L., Mann D.A. Clinical evidence for the regression of liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 2012;56:1171–1180. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports注册入口" Full Text Sources
Research Materials
V体育ios版 - Miscellaneous

