VSports在线直播 - Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35632728
- PMCID: PMC9146458
- DOI: 10.3390/v14050986 (V体育2025版)
V体育2025版 - Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
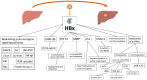
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is DNA-based virus, member of the Hepadnaviridae family, which can cause liver disease and increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in infected individuals, replicating within the hepatocytes and interacting with several cellular proteins. Chronic hepatitis B can progressively lead to liver cirrhosis, which is an independent risk factor for HCC. Complications as liver decompensation or HCC impact the survival of HBV patients and concurrent HDV infection worsens the disease. The available data provide evidence that HBV infection is associated with the risk of developing HCC with or without an underlying liver cirrhosis, due to various direct and indirect mechanisms promoting hepatocarcinogenesis. The molecular profile of HBV-HCC is extensively and continuously under study, and it is the result of altered molecular pathways, which modify the microenvironment and lead to DNA damage. HBV produces the protein HBx, which has a central role in the oncogenetic process VSports手机版. Furthermore, the molecular profile of HBV-HCC was recently discerned from that of HDV-HCC, despite the obligatory dependence of HDV on HBV. Proper management of the underlying HBV-related liver disease is fundamental, including HCC surveillance, viral suppression, and application of adequate predictive models. When HBV-HCC occurs, liver function and HCC characteristics guide the physician among treatment strategies but always considering the viral etiology in the treatment choice. .
Keywords: hepatitis B; hepatitis B chronic hepatitis; hepatitis B virus; hepatitis D virus; hepatocellular carcinoma. V体育安卓版.
"VSports手机版" Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
"V体育官网" References
-
- De Flora S.C.E., Bonanni P., Ferro A., Vitale F. Vaccines and Cancer Prevention/Screening Working Groups of the Italian Society of Hygiene, Preventive Medicine and Public Health (SItI). Incidence of infection-associated cancers in Italy and prevention strategies. Epidemiol. Prev. 2015;39:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Vitale A., Svegliati-Baroni G., Ortolani A., Cucco M., Dalla Riva G.V., Giannini E.G., Piscaglia F., Rapaccini G., Di Marco M., Caturelli E., et al. Epidemiological trends and trajectories of MAFLD-associated hepatocellular carcinoma 2002–2033: The ITA.LI.CA database. Gut. 2021. ahead of print . - DOI - PubMed
V体育2025版 - Publication types
- Actions (V体育ios版)
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
VSports最新版本 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical